| CPC H01M 10/484 (2013.01) [B60L 58/12 (2019.02); G01R 31/3842 (2019.01); H01M 50/569 (2021.01); H01M 2220/20 (2013.01)] | 4 Claims |
|
1. A rechargeable battery state determination method that determines whether a rechargeable battery is in a micro-short-circuit-prone state, which is a state that is highly likely to form a micro-short circuit, the rechargeable battery state determination method, comprising:
measuring an electron transfer resistance of the rechargeable battery by applying a voltage or current having a predetermined or higher frequency to an electrode system of the rechargeable battery, wherein:
the electron transfer resistance of the rechargeable battery is correlated with an inter-electrode distance of the rechargeable battery and an amount of an electrolytic solution contained in a separator of the rechargeable battery; and
the measuring an electron transfer resistance of the rechargeable battery includes:
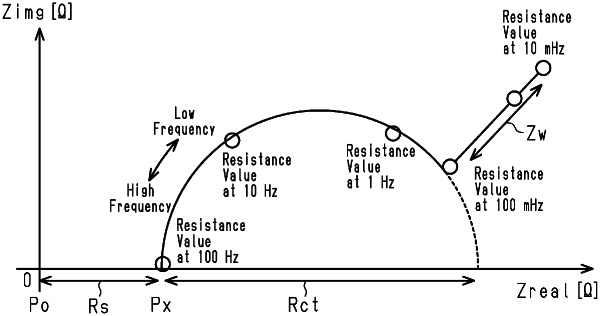
outputting a Nyquist plot by applying a voltage or current to the electrode system of the rechargeable battery as a frequency with very small amplitude is changed in a stepped manner to measure impedance spectrum of the rechargeable battery using an alternating current impedance method; and
obtaining a real value of a zero cross expressing the electron transfer resistance of the rechargeable battery from the outputted Nyquist plot;
determining whether the inter-electrode distance is satisfactory based on a comparison of the measured electron transfer resistance of the rechargeable battery with a predetermined lower limit threshold value, the determining whether an inter-electrode distance is satisfactory including determining that the inter-electrode distance is satisfactory when the measured electron transfer resistance of the rechargeable battery is greater than or equal to the lower limit threshold value;
determining whether the amount of the electrolytic solution contained in the separator is satisfactory based on a comparison of the measured electron transfer resistance of the rechargeable battery with a predetermined upper limit threshold value, the determining whether the amount of the electrolytic solution contained in the separator is satisfactory includes determining that the amount of the electrolytic solution contained in the separator is satisfactory when the measured electron transfer resistance of the rechargeable battery is less than the predetermined upper limit threshold value; and
determining that the rechargeable battery is a conforming piece when the inter-electrode distance and the amount of the electrolytic solution contained in the separator are satisfactory.
|