| CPC G16H 20/70 (2018.01) [A61B 3/113 (2013.01); A61B 5/162 (2013.01); A61B 5/163 (2017.08); G06F 7/588 (2013.01); A61B 5/168 (2013.01)] | 10 Claims |
|
1. A processor implemented method, comprising:
assigning, by one or more hardware processors, a primary executive task to a subject, wherein the primary executive task is generation of random numbers by the subject to obtain human generated random numbers;
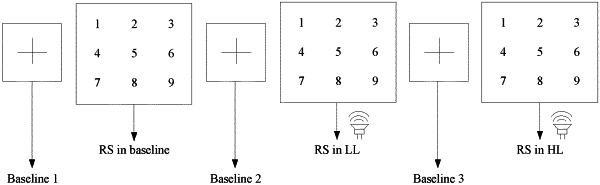
digitizing, by the one or more hardware processors, the human generated random numbers into a first random sequence (RS) in a baseline by concatenating the human generated random numbers until:
capture of a specific number of the generated random numbers, or
capture of the generated random numbers in a specific time period, wherein
the first RS in the baseline is digitized after a first baseline period, and
the first baseline period is a time period after the generation of the random numbers;
generating, after the primary executive task, a second RS in a low load (LL) and a third RS in a high load (HL), by the one or more hardware processors, by imposing a secondary cognitive load task in a form of:
a low cognitive load inducing task on the subject, and
a high cognitive load inducing task on the subject, wherein
the secondary cognitive load task includes auditory addition of a plurality of auditory digits,
the low cognitive load inducing task includes the auditory addition of a plurality of first specific auditory digits of the plurality of auditory digits,
the high cognitive load inducing task includes the auditory addition of a plurality of second specific auditory digits of the plurality of auditory digits,
a count of the plurality of second specific auditory digits is greater than a count of the plurality of first specific auditory digits,
an auditory digit of the plurality of auditory digits is presented at a rate of 1 auditory digit per 3 seconds for the low cognitive load inducing task,
the auditory digit of the plurality of auditory digits is presented at a rate of 1 auditory digit per 4 seconds for the high cognitive load inducing task,
the low cognitive load inducing task is preceded by a first pause for a second baseline period, wherein the second baseline period is a time period after the digitization of the RS in the baseline,
the high cognitive load inducing task is preceded by a second pause for a third baseline period, wherein the third baseline period is a time period after completion of the low cognitive load inducing task, and
each of the second baseline period and the third baseline period allows the subject to relax;
receiving, by the one or more hardware processors, gaze data and pupillometry data associated with the subject, from an eye tracker, wherein each of the gaze data and the pupillometry data is specific data that is received during performance of both the primary executive task and the secondary cognitive load task by the subject;
extracting gaze related fixation patterns, by the one or more hardware processors, from the received gaze data by separating fixation points of the gaze data and saccade points of the gaze data based on point-to-point velocities in the gaze data, wherein
the fixation patterns are extracted for each of the first RS in the baseline, the second RS in the LL, and the third RS in the HL,
the fixation points include a plurality of points of the gaze data having a first velocity that is lesser than a specific threshold, and
the saccade points include a second plurality of points of the gaze data having a second velocity that is equal to or greater than the specific threshold; and
computing, for each of the first RS in the baseline, the second RS in the LL, and the third RS in the HL, by the one or more hardware processors, a load index (A) by calculating a ratio of:
a product of summation of a length of repeating fixation of the fixation patterns of the extracted gaze data and a total length of random sequence, and
a total number of fixations of the gaze data, wherein
the load index indicates an effect of the secondary cognitive load task on the primary executive task, and
a value of the load index is directly proportional to the effect of the secondary cognitive load task on the primary executive task.
|