| CPC G06N 7/01 (2023.01) [G06F 30/367 (2020.01); G06N 20/00 (2019.01)] | 17 Claims |
|
1. A method comprising:
by a computing system:
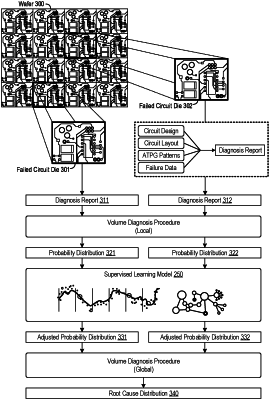
accessing a diagnosis report for a given circuit die that has failed scan testing;
computing, through a local phase of a volume diagnosis procedure, a probability distribution for the given circuit die from the diagnosis report, wherein the probability distribution specifies probabilities for different suspect root causes as having caused the given circuit die to fail;
adjusting the probability distribution into an adjusted probability distribution using a supervised learning model, including by, through the supervised learning model, changing at least one of the probabilities for the different suspect root causes specified in the probability distribution as having caused the given circuit die to fail through the supervised learning model, the supervised learning model trained with a training set comprising training probability distributions of suspect root causes computed from training dies through the local phase of the volume diagnosis procedure, the training dies injected with particular root causes that cause the training dies to fail, and each training probability distribution of suspect root causes of the training set labeled with an actual root cause, wherein the actual root cause specifies the particular root cause injected into a given training die that caused the given training die to fail;
providing the adjusted probability distribution for the given circuit die as an input to a global phase of the volume diagnosis procedure to determine a global root cause distribution for multiple circuit dies that have failed the scan testing;
performing the global phase of the volume diagnosis procedure using, as inputs, a plurality of adjusted probability distributions from the multiple circuit dies that have failed the scan testing, including the adjusted probability distribution for the given circuit die adjusted through the supervised learning model; and:
generating the supervised learning model, including by
accessing the training dies, wherein each training die has been injected with a respective specific root cause to actually cause a scan test failure;
generating diagnosis reports for each of the training dies;
computing, through the local phase of a volume diagnosis procedure, the training probability distributions of suspect root causes from the diagnosis reports generated for the training dies, each of the training probability distributions of suspect root causes respectively corresponding to one of the training dies;
labeling each of the training probability distributions of suspect root causes with the respective specific root cause for the training die corresponding to the training probability distribution of suspect root causes, wherein the respective specific root cause specifies the actual root cause injected into the training die to cause the training die to fail; and
providing, as the training set, the labeled training probability distributions to train the supervised learning model.
|