| CPC G06N 3/0675 (2013.01) [G02F 1/00 (2013.01); G02F 3/024 (2013.01); G06E 1/045 (2013.01); G06E 3/005 (2013.01); G06E 3/006 (2013.01); G06E 3/008 (2013.01); G06F 17/14 (2013.01); G06F 17/16 (2013.01); G06N 3/08 (2013.01); G02F 1/225 (2013.01)] | 30 Claims |
|
1. A system, comprising:
a first unit configured to generate a plurality of modulator control signals;
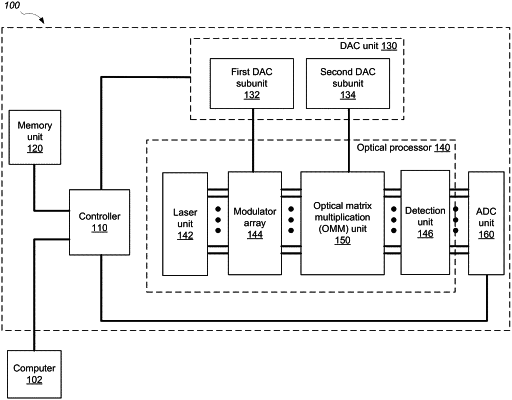
a processor unit comprising:
a light source configured to provide a plurality of light outputs;
a plurality of optical modulators coupled to the light source and the first unit, the plurality of optical modulators being configured to generate an optical input vector by modulating the plurality of light outputs provided by the light source based on the plurality of modulator control signals, the optical input vector comprising a plurality of optical signals; and
a matrix multiplication unit coupled to the plurality of optical modulators and the first unit, the matrix multiplication unit being configured to transform the optical input vector into an analog output vector based on a plurality of weight control signals;
a second unit coupled to the matrix multiplication unit and configured to convert the analog output vector into a digitized output vector; and
a controller comprising integrated circuitry configured to perform operations comprising:
receiving an artificial neural network computation request comprising an input dataset that comprises a first digital input vector;
receiving a first plurality of neural network weights; and
generating, through the first unit, a first plurality of modulator control signals based on the first digital input vector and a first plurality of weight control signals based on the first plurality of neural network weights;
wherein the first unit, the processor unit, the second unit, and the controller are used in an optoelectronical processing loop that is repeated for a plurality of iterations, and the optoelectronical processing loop includes:
(1) at least a first optical modulation operation based on at least one of the plurality of modulator control signals, and at least a second optical modulation operation based on at least one of the weight control signals, and
(2) an electrical summation operation.
|