| CPC G06N 3/045 (2023.01) [G06T 7/0012 (2013.01); G06T 2207/10056 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A method comprising:
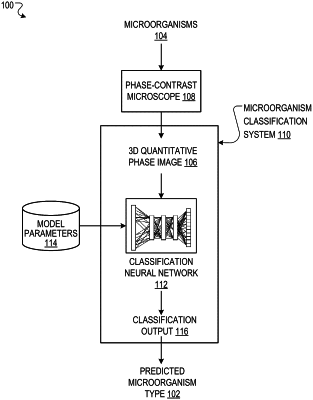
using a phase-contrast microscope to generate one or more three-dimensional (3D) quantitative phase images of one or more microscopic entities,
wherein each of the 3D quantitative phase images comprises a respective 3D representation of the one or more microscopic entities as a 3D refractive index tomogram represented as a 3D matrix of numerical values, where each component of the 3D matrix corresponds to a respective 3D spatial position and defines a refractive index at the corresponding 3D spatial position; and
processing the one or more 3D quantitative phase images using a neural network, wherein:
the neural network is a convolutional neural network comprising one or more 3D convolutional layers, wherein each of the 3D convolutional layers performs operations comprising:
receiving a layer input that comprises one or more 3D matrices of features derived from the one or more 3D quantitative phase images input to the neural network; and
processing the layer input to generate a layer output, comprising convolving one or more 3D convolutional filters with the one or more 3D matrices included in the layer input; and
the neural network is configured to process the one or more three-dimensional quantitative phase images in accordance with trained parameter values of the neural network to generate a neural network output characterizing the one or more microscopic entities; and
classifying the one or more microscopic entities using the neural network output.
|