| CPC G01C 19/5776 (2013.01) [E02F 9/26 (2013.01); G01C 25/00 (2013.01)] | 15 Claims |
|
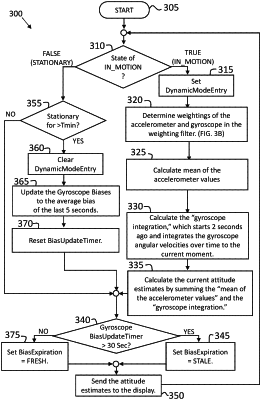
1. A method for improved control of a vehicle based on reliably determining whether the vehicle is in motion by an Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) mounted on the vehicle, the method comprising:
calculating, by a processor system of the IMU, a differential change in angular velocity for a gyroscope axis;
comparing, by the processor system, the differential change to a predetermined differential velocity threshold;
in response to determining that the differential change is less than the predetermined differential velocity threshold, calculating, by the processor system, a total variance of the angular velocity for the gyroscope axis over a time window, wherein the total variance is calculated using a sum of squares of differences between sequential gyroscope readings, wherein the sequential gyroscope readings are measured over a 50-millisecond time frame;
in response to determining that the total variance is greater than a predetermined standard deviation threshold, determining, by the processor system, that the vehicle is in motion;
setting, by the processor system, an in-motion flag based on the determination that the vehicle is in motion;
controlling, by the processor system, a display device to display an indication of the determination that the vehicle is in motion;
utilizing, by the processor system, the determination that the vehicle is in motion in calculating an attitude adjustment;
determining, by the processor system, real-time spatial orientation of the vehicle based on the calculated attitude adjustment;
controlling, by the processor system, the display device to display the real-time spatial orientation of the vehicle; and
controlling, by the processor system, the vehicle based at least in part on the real-time spatial orientation.
|