| CPC C07C 4/22 (2013.01) [B01D 3/143 (2013.01); B01D 3/4227 (2013.01); C07C 7/04 (2013.01); C08J 11/12 (2013.01); C10B 53/07 (2013.01); C08J 2325/06 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
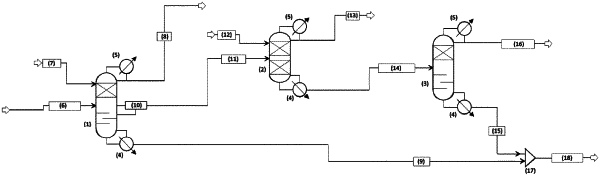
|
1. A process for retrieving styrenic monomer from a polymer mixture (P),
the polymer mixture (P) comprising:
(A) 1 wt-% to 99.8 wt-%, related to the total weight of polymer mixture (P),
of a styrenic polymer comprising:
i. 70 wt-% to 100 wt-%, related to the total weight of (A), of repeating units derived from a styrenic monomer selected from styrene and alpha-methylstyrene;
ii. 0 wt-% to 30 wt-%, related to the total weight of (A), of repeating units derived from dienes;
iii. 0 wt-% to 2 wt-%, related to the total weight of (A), of repeating units derived from other radically co-polymerizable monomers;
(B) 0.1 wt-% to 98.9 wt-%, related to the total weight of polymer mixture (P), of a mixture of polymers other than polymer (A);
(C) 0.1 wt-% to 30 wt-%, related to the total weight of polymer mixture (P), of organic or inorganic polymer additives and auxiliaries; and optionally
(D) 0 wt-% to 50 wt-%, related to the total weight of polymer mixture (P), of impurities such as, but not limited to, food waste, dirt, packaging residues or moisture,
the process comprising the steps of:
I) feeding the polymer mixture (P) into a pyrolysis zone of a pyrolysis reactor and subjecting it to a temperature of 300° C. to 650° C., measured as the average temperature of the polymer mixture (P) at the inner surface of the reactor wall during the reaction runtime, during which at least partial decomposition of the component (A) to styrenic monomers takes place, and a gas containing said styrenic monomers is formed;
II) condensing the condensable substances including styrenic monomers from the gas formed in step I) at a cooling rate of more than 500° C./min (500 K/min);
III) fractionating the condensed substances from step II) in a distillation column (X),
wherein in step III),
a fraction (a1) comprising styrenic monomers is withdrawn through a side outlet from the distillation column (X), at a position above 65% to 95% and below 35% to 5% of the total number of theoretical stages;
a fraction (a2) comprising heavy boilers is collected at the bottom of the distillation column (X);
a fraction (a3) comprising light boilers is collected at the head of the distillation column (X); and
the distillation column (X) is operated at a bottom pressure of 200 hPa (150 mmHg) to 533 hPa (400 mmHg), a head pressure of 133 hPa (100 mmHg) to 400 hPa (300 mmHg), a bottom temperature of 200° C. to 300° C., and a head temperature of 40° C. to 80° C.
|