| CPC C02F 1/008 (2013.01) [C02F 1/66 (2013.01); C02F 1/686 (2013.01); C02F 1/70 (2013.01); C02F 1/763 (2013.01); C02F 1/766 (2013.01); C02F 2103/42 (2013.01); C02F 2209/006 (2013.01); C02F 2209/02 (2013.01); C02F 2209/04 (2013.01); C02F 2209/06 (2013.01); C02F 2209/44 (2013.01); C02F 2303/04 (2013.01); C02F 2303/185 (2013.01)] | 42 Claims |
|
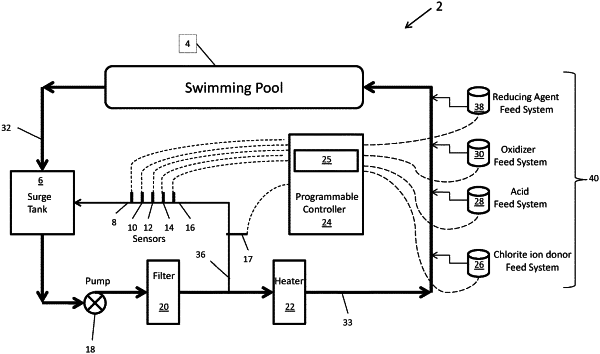
1. A method for accelerating remediation of pathogens resistant to chlorine in water of an aquatic facility having a conduit connected to the water in the aquatic facility, the method comprising:
providing a programmable controller interfaced with an oxidizer feed system and a chlorite ion donor feed system;
implementing an accelerated remediation cycle by the programmable controller;
the programmable controller activating the oxidizer feed system and the chlorite ion donor feed system to supply an oxidizing agent and a chlorite ion donor to the conduit to achieve localized high concentrations of the oxidizing agent and the chlorite ion donor, wherein chlorine dioxide is produced in the conduit by a cyclic process comprising activating bromide ions with the oxidizing agent to produce free bromine, the free bromine oxidizing chlorite ions to produce the chlorine dioxide, and reducing at least a portion of the free bromine back to the bromide ions repeating the cyclic process;
supplying the chlorine dioxide from the conduit to the water; and
measuring a concentration of the chlorine dioxide in the water by a chlorine dioxide sensor in communication with the programmable controller;
the programmable controller recording the chlorine dioxide concentration in the water;
the programmable controller calculating a chlorine dioxide Ct value of the water in real time;
the programmable controller sustaining the concentration of the chlorine dioxide in the water until a targeted chlorine dioxide Ct value of the water is reached to achieve remediation of the water, wherein the remediation is at least a 3-log reduction of at least one pathogen resistant to the chlorine in the water.
|