| CPC B81C 1/00158 (2013.01) [B81B 3/0021 (2013.01); B81B 2203/0127 (2013.01); H04R 2201/003 (2013.01)] | 22 Claims |
|
1. An electromechanical microsystem comprising:
at least one electromechanical transducer comprising a portion movable between a balance position, off-load, and an out-of-balance position, under load,
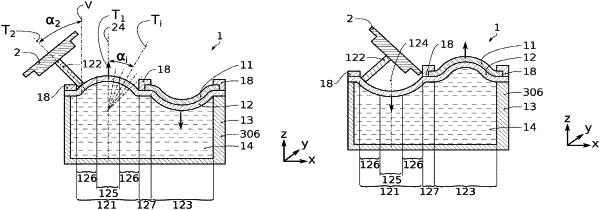
at least one deformable diaphragm,
a first deformable cavity, delimited by walls, at least one portion of the deformable diaphragm forming at least one portion of a first wall selected amongst said walls of the cavity, the cavity being configured to hermetically contain a deformable medium capable of keeping a substantially constant volume under the action of a change of an external pressure exerted on the deformable medium through one of the walls of the cavity,
wherein the movable portion of the electromechanical transducer is configured so that its movement depends on said change in the external pressure, or conversely its movement induces a change in the external pressure, and wherein said at least one portion of the deformable diaphragm has at least one free area freely deformable, elastically, as a function of said change in the external pressure, the free area having an outer perimeter and a peripheral portion which extends from the outer perimeter and up to a central portion of the free area,
the electromechanical microsystem comprising at least one pin, configured to bear on the peripheral portion of the free area so that a deformation of the free area of the diaphragm causes an inclination of the pin.
|