| CPC A61B 5/055 (2013.01) [A61B 5/0816 (2013.01); A61B 5/113 (2013.01); A61B 5/7235 (2013.01); A61B 5/7264 (2013.01); A61B 5/7267 (2013.01); A61B 5/7271 (2013.01); A61B 5/7275 (2013.01); A61B 5/7292 (2013.01); A61B 5/7285 (2013.01)] | 19 Claims |
|
1. A method for determining a respiration phase of a respiration signal, comprising:
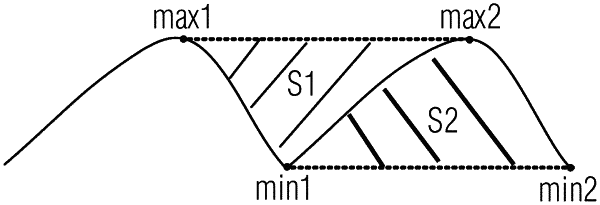
extracting, via one or more processors, a distance characteristic value, a score characteristic value, and an area characteristic value from the respiration signal, the distance characteristic value, the score characteristic value, and the area characteristic value indicating a waveform variation between two adjacent waveforms in the respiration signal;
training, via one or more processors, a respiration signal model according to the distance characteristic value, the score characteristic value, and the area characteristic value;
determining, via one or more processors, the respiration phase of the respiration signal using the respiration signal model; and
performing, via a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) apparatus, magnetic resonance imaging of an examination region of an examination subject using the determined respiration phase,
wherein the area characteristic value represents a ratio of (i) an area formed by two crest points of the two adjacent waveforms in the respiration signal and a trough point between the two adjacent waveforms in the respiration signal to (ii) an area formed by a second waveform of the two adjacent waveforms in the respiration signal.
|