| CPC H04N 19/577 (2014.11) [H04N 19/107 (2014.11); H04N 19/109 (2014.11); H04N 19/11 (2014.11); H04N 19/119 (2014.11); H04N 19/136 (2014.11); H04N 19/17 (2014.11); H04N 19/174 (2014.11); H04N 19/176 (2014.11); H04N 19/44 (2014.11); H04N 19/593 (2014.11); H04N 19/61 (2014.11); H04N 19/70 (2014.11); H04N 19/82 (2014.11); H04N 19/86 (2014.11); H04N 19/895 (2014.11)] |
| AS A RESULT OF REEXAMINATION, IT HAS BEEN DETERMINED THAT: |
| Claims 23 and 24 are cancelled. |
| Claims 1, 13, 15, 19, 22, 25-28 are determined to be patentable as amended. |
| Claims 8 and 11-12, dependent on an amended claim, are determined to be patentable. |
| New claims 32-51 are added and determined to be patentable. |
| Claims 2-7, 9-10, 14, 16-18, 20-21 and 29-31 were not reexamined. |
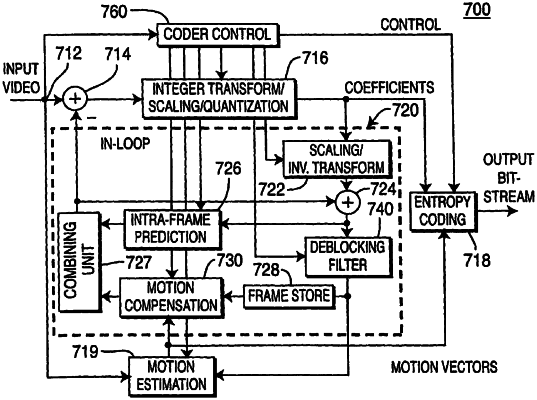
|
1. In a video encoder, a method for video encoding a block comprising: [ additively ] combining a first prediction of a current block with a second prediction of
wherein the current block includes a group of pixels, the first prediction being of at least one pixel of the group of pixels and the second prediction being of the at least one pixel of the group of pixels.]
|
|
13. In a video encoder, a method of video encoding for compressing and encoding frames of a two-dimensional image sequence for transmission comprising: dividing a frame of the image sequence into blocks, selecting blocks and encoding the selected blocks in a bi-predictive hybrid intra-inter encoding mode into a bitstream for transmission [ ;
wherein encoding a current block of the selected blocks in a bi-predictive hybrid intra-inter encoding mode includes additively combining a first prediction of the current block with a second prediction of the current block; wherein the first prediction of the current block is intra prediction and the second prediction of the current block is inter prediction;
wherein the current block includes a group of pixels, the first prediction being of at least one pixel of the group of pixels and the second prediction being of the at least one pixel of the group of pixels.]
|
|
15. A video encoder for encoding blocks within frames of a sequence of two dimensional images, the encoder comprising: an intra-frame prediction block being operatively connected to a combining unit and for outputting a first intra prediction of a block; and an inter-frame prediction block being operatively connected to the combining unit and for outputting a first inter prediction of the block; wherein the combining unit is adapted to [ additively ] combine the first intra prediction and the first inter prediction and to output a hybrid intra-inter coded block [ ;
wherein the block includes a group of pixels, the first intra prediction being of at least one pixel of the group of pixels and the first inter prediction being of the at least one pixel of the group of pixels.]
|
|
19. The video encoder of claim 15, wherein the intra-frame prediction block is adapted to output a second intra prediction of the block
|
|
22. A video encoder for compressing and encoding frames of a two dimensional image sequence for transmission, the video encoder being adapted to select blocks from at least one frame of the image sequence and to encode the selected blocks
the video encoder being adapted to, in the bi-predictive hybrid intra-inter encoding mode, encode a current block of the selected blocks by at least additively combining a first prediction of the current block with a second prediction of the current block; wherein the first prediction of the current block is intra prediction and the second prediction of the current block is inter prediction;
wherein the current block includes a group of pixels, the first prediction being of at least one pixel of the group of pixels and the second prediction being of the at least one pixel of the group of pixels.]
|
|
25. The video encoder of claim 22 wherein
|
|
26. The video encoder of claim 22 wherein
|
|
27. A multimedia terminal, comprising a video encoder adapted to encode a digital video sequence using motion compensated prediction, said digital video sequence comprising a number of frames, wherein the video encoder is adapted to select blocks from at least one frame of the image sequence and to encode the selected blocks; wherein encoding each of the blocks includes [ additively ] combining a first prediction and a second prediction, wherein the encoder is further adapted to select for encoding one of the selected blocks, between an intra encoding mode of the related art, an inter encoding mode of the related art, and a bi-predictive hybrid intra-inter encoding mode
[ the video encoder being adapted to, in the bi-predictive hybrid intra-inter encoding mode, encode a current block of the selected blocks by at least combining a first prediction of the current block with a second prediction of the current block; wherein the first prediction of the current block is intra prediction and the second prediction of the current block is inter prediction;
wherein the current block includes a group of pixels, the first prediction being of at least one pixel of the group of pixels and the second prediction being of the at least one pixel of the group of pixels.]
|
|
28. In a video encoder, a method for video encoding a block comprising: [ additively ] combining a first prediction type for a current block with a second prediction type for a current block; wherein the combination of the first prediction type and the second prediction type forms a hybrid prediction type [ ;
wherein the current block includes a group of pixels, the first prediction type including a first prediction of at least one pixel of the group of pixels and the second prediction type including a second prediction of the at least one pixel of the group of pixels.]
|
|
[ 32. In a video encoder, a method for video encoding a block comprising:
combining a first prediction of a current block with a second prediction of the current block;
wherein the first prediction of the current block is intra prediction and the second prediction of the current block is inter prediction;
wherein the first prediction and the second prediction are combined by averaging the first prediction and the second prediction.]
|
|
[ 33. The method of claim 32, wherein encoding the block includes combining the first prediction and the second prediction and a third prediction of the current block.]
|
|
[ 34. The method of claim 32, wherein the current block is coded as a Direct mode block.]
|
|
[ 35. The method of claim 32, further comprising reducing the filter strength of a deblocking filter adapted to increase the correlation between pixels adjacent to the current block.]
|
|
[ 36. The method of claim 32, wherein the current block is a 16×16 macroblock.]
|
|
[ 37. The method of claim 32, wherein the current block is a sub-macroblock.]
|
|
[ 38. The method of claim 32, wherein the current block is a 4×4 sub-macroblock partition.]
|
|
[ 39. A non-transitory computer-usable medium having a computer-readable program code embodied therein for causing a computer system to perform the method of claim 32.]
|
|
[ 40. A non-transitory recording medium that stores a program, readable by a computer, for causing a computer system to perform the method of claim 32.]
|
|
[ 41. In a video encoder, a method for video encoding a block comprising:
additively combining a first prediction of a current block with a second prediction of a current block;
wherein the first prediction of the current block is intra prediction and the second prediction of the current block is inter prediction;
wherein the first prediction and the second prediction are combined by weighting each of the first prediction and the second prediction.]
|
|
[ 42. The method of claim 41, wherein encoding the block includes combining the first prediction and the second prediction and a third prediction of the current block.]
|
|
[ 43. The method of claim 41, wherein the current block is coded as a Direct mode block.]
|
|
[ 44. The method of claim 41, further comprising reducing the filter strength of a deblocking filter adapted to increase the correlation between pixels adjacent to the current block.]
|
|
[ 45. The method of claim 41, wherein the current block is a 16×16 macroblock.]
|
|
[ 46. The method of claim 41, wherein the current block is a sub-macroblock.]
|
|
[ 47. The method of claim 41, wherein the current block is a 4×4 sub-macroblock partition.]
|
|
[ 48. A non-transitory computer-usable medium having a computer-readable program code embodied therein for causing a computer system to perform the method of claim 41.]
|
|
[ 49. A non-transitory recording medium that stores a program, readable by a computer, for causing a computer system to perform the method of claim 41.]
|
|
[ 50. The method of claim 1, wherein the first prediction of the current block and the second prediction of the current block include at least one common pixel location.]
|
|
[ 51. The method of claim 1, wherein the first prediction of the current block includes predicted pixel values for all pixels located within the current block.]
|