| CPC H04W 12/12 (2013.01) [G06F 18/00 (2023.01); G06N 3/08 (2013.01); G06Q 20/10 (2013.01); G06Q 20/4016 (2013.01); H04W 16/18 (2013.01); H04W 24/08 (2013.01); H04W 24/10 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A computer-implemented method comprising:
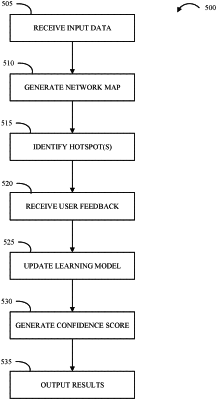
receiving, by a processor, input data, wherein the input data includes a plurality of messages, each message containing a set of message data;
generating, by a pattern detector and based on the plurality of messages, a network graph;
analyzing the network graph to identify one or more hotspots, wherein each hotspot of the one or more hotspots is identified as a scenario that includes potentially fraudulent activity;
identifying, in the network graph and by a learning model, a first hotspot of the one or more hotspots;
compiling a set of hotspot characteristics for the first hotspot, wherein the identifying of the first hotspot is based a first characteristic of the set of characteristics;
indicating, to a user through a network interface, the first hotspot;
receiving, in response to identifying and indicating the first hotspot and in response to a review of the hotspot characteristics for the first hotspot, a first user feedback, wherein the first user feedback includes a level of agreement and the first hotspot includes the potentially fraudulent activity;
updating, based on the first user feedback, the learning model, wherein the updating is configured to reduce a number of false positive hot spots;
generating, by the learning model and based in part on the first user feedback, a hotspot confidence score for the first hotspot; and
outputting, by the network interface, the hotspot confidence score and the network graph.
|