| CPC H04L 5/16 (2013.01) [H04L 5/0051 (2013.01); H04L 5/0055 (2013.01); H04W 72/0446 (2013.01)] | 29 Claims |
|
1. A method for wireless communication at a user equipment (UE), comprising:
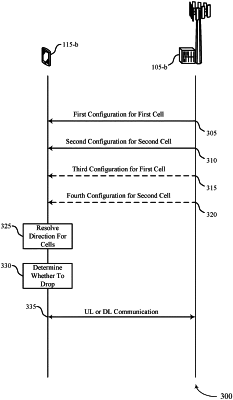
receiving a first slot format configuration for a first serving cell for at least a transmission time interval (TTI), the first slot format configuration indicating a first plurality of communication directions for the TTI, the first plurality of communication directions including at least a first communication direction for a first transmission on the first serving cell;
receiving a second slot format configuration for a second serving cell for at least the TTI, the second slot format configuration indicating a second plurality of communication directions for the TTI on the second serving cell, the second plurality of communication directions including at least a second communication direction for a second transmission on the second serving cell, wherein the second communication direction is different from the first communication direction, and wherein the second transmission is scheduled to at least partially overlap in time with the first transmission; and
communicating the first transmission on the first serving cell in the first communication direction and dropping the second transmission on the second serving cell in the second communication direction TTI based at least in part on the first communication direction being different from the second communication direction.
|