| CPC H02K 33/16 (2013.01) [B06B 1/045 (2013.01); G08B 6/00 (2013.01); H02K 11/0141 (2020.08)] | 23 Claims |
|
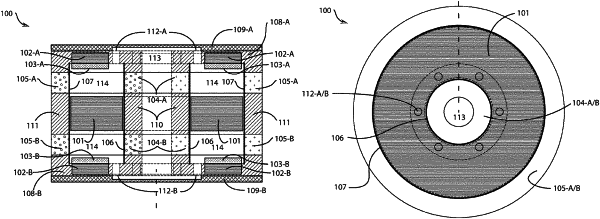
1. A transducer configured to convert electrical signals into vibrational movement, the transducer comprising:
an axially-magnetised reciprocating magnet magnetically suspended between first and second axially-magnetised stationary magnets located on opposing sides of the axially-magnetised reciprocating magnet, wherein the axially-magnetised reciprocating magnet comprises an aperture such that the reciprocating magnet has an inner boundary and an outer boundary; and
at least two pairs of concentrically positioned electromagnetic solenoids, the at least two pairs of concentrically positioned electromagnetic solenoids being configured to drive the reciprocating magnet to reciprocate in a volume between the first and second axially-magnetised stationary magnets,
wherein a first solenoid of each of the pairs of concentrically positioned electromagnetic solenoids is positioned to influence the reciprocating magnet at the inner boundary more than at the outer boundary, and a second solenoid of each of the pairs of concentrically positioned electromagnetic solenoids is positioned to influence the reciprocating magnet at the outer boundary more than at the inner boundary.
|