| CPC G06T 7/55 (2017.01) [G06F 17/16 (2013.01); G06F 18/214 (2023.01); G06N 20/00 (2019.01); G06T 15/10 (2013.01); G06T 17/205 (2013.01)] | 2 Claims |
|
1. A processor, comprising:
logic to predict one or more three-dimensional (3D) meshes based on a plurality of digital images, wherein the one or more 3D meshes are refined using a trained decoder based on differences between the one or more 3D meshes and the plurality of digital images;
wherein predicting the one or more 3D meshes based on the plurality of digital images comprises:
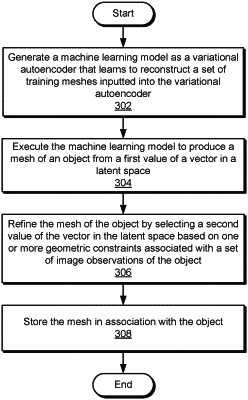
executing the decoder to produce a mesh of an object from a first value in a latent space; and
refining the mesh of the object using the decoder, wherein refining the mesh of the object comprises selecting a second value in the latent space based on one or more geometric constraints associated with the plurality of digital images of the object;
wherein refining the mesh of the object comprises:
dividing the mesh into a set of meshlets;
for each meshlet in the set of meshlets, selecting the second value in the latent space to learn a prior for a portion of the mesh represented by the meshlet; and
reconstructing the mesh from the set of meshlets; and
wherein refining the mesh of the object further comprises iteratively increasing a resolution of the set of meshlets to meet the one or more geometric constraints.
|