| CPC G06F 11/1068 (2013.01) [G06F 11/0772 (2013.01); G06F 11/0793 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
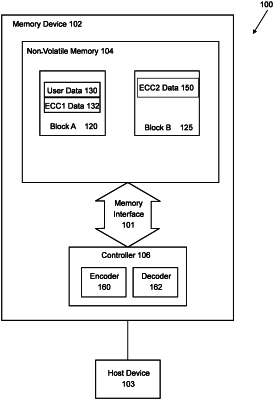
1. A system, comprising:
a non-volatile memory configured to store data in memory cells; and
a controller configured to:
provide user data and first error correction code data in a first block of the non-volatile memory, wherein the first error correction code data provides a capability for correcting at least one error in the user data;
provide second error correction code data in a second block of the non-volatile memory, wherein the second error correction code data provides an additional capability for correcting the at least one error in the user data;
determine whether a stress event affecting the non-volatile memory has completed;
scan, based on the stress event being determined to be completed, the user data in the first block;
determine, based on the scanning, whether the first block of the non-volatile memory is capable of satisfying a threshold reliability requirement without utilizing the second error correction code data in the second block;
execute, based on the first block being determined to not be capable of satisfying the threshold reliability requirement, a touch-up process on the first block to reinstate an operating state of the first block such that the second block is no longer needed for error correction of the user data; and
delete the second error correction code data from the second block, thereby retrieving capacity of the second block of the non-volatile memory.
|