| CPC G01N 1/312 (2013.01) [G01N 35/00029 (2013.01); G01N 2035/00039 (2013.01)] | 35 Claims |
|
1. A method for analyzing a biological sample, the method comprising:
obtaining a biological sample mounted on a first substrate;
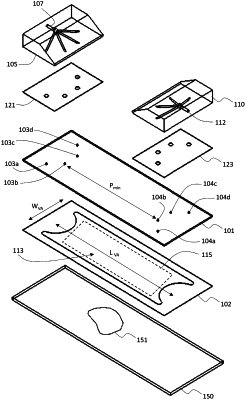
affixing a second substrate to the first substrate to form an enclosed chamber on the first substrate with the biological sample positioned within an interior volume of the enclosed chamber, wherein the second substrate comprises a first port formed by a first aperture extending through a thickness of the second substrate and a second port formed by a second aperture extending through the thickness of the second substrate;
introducing a composition into the interior volume through the first port, wherein the composition comprises multiple different types of capture agents, each of the different types of capture agents comprising a different type of binding agent that selectively binds to a different sample component and an oligonucleotide linked to the binding agent that is specific to each different type of binding agent, wherein each of the different types of capture agents is bound to the biological sample by introducing the different types of capture agents at the same time into the interior volume of the enclosed chamber; and
performing multiple imaging cycles, wherein each imaging cycle comprises:
(a) binding a probe to the biological sample;
(b) obtaining an image of the bound probe in the biological sample; and
(c) removing at least a portion of the probe from the biological sample,
wherein a thickness of the interior volume between the first and second substrates is 250 micrometers or less.
|