| CPC F04B 49/22 (2013.01) [F04B 25/02 (2013.01); F04B 49/007 (2013.01); F04B 49/20 (2013.01)] | 6 Claims |
|
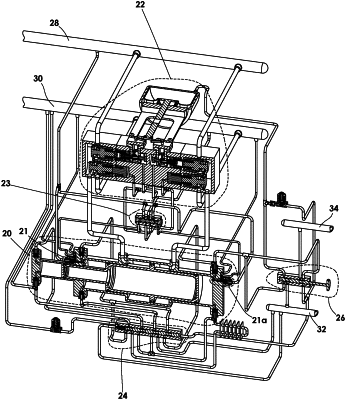
1. A system that enables captured fugitive gas emissions consisting primarily of methane gas to be compressed such that the captured fugitive gas emissions are re-introduced into a natural gas pipeline system, comprising:
a pump, containing one or more cylinders containing one or more pistons with a major diameter in a center of the one or more cylinders and two or more minor diameters situated distally opposed from the center in an axial direction, wherein diameters are concentric within the one or more cylinders, wherein each end of the one or more cylinders contains a cylinder head configured for suctioning and discharging said captured fugitive gas emissions with movement of the one or more pistons;
a drive section inlet, said drive section inlet being coupled to said natural gas pipeline system on a high pressure side of at least one natural gas compressor, said drive section inlet operable to facilitate introduction of compressed natural gas from said natural gas pipeline system into the drive section of the pump;
a drive section discharge port, said drive section discharge port being operably coupled to a low pressure side of said at least one natural gas compressor;
a captured fugitive emissions gas inlet, said captured fugitive emissions gas inlet being operably coupled to receive gas from a captured fugitive emissions source, said captured fugitive emissions gas inlet having tubing coupled thereto, said tubing configured to direct gas into the captured fugitive emissions gas inlet;
a captured fugitive emissions compressed gas discharge port, said captured fugitive emissions compressed gas discharge port being operably coupled to said low pressure side of said at least one natural gas compressor;
a selector valve fluidly connected to the pump, said selector valve operably coupled to isolated pipe sections upstream and downstream of one compressor of the at least one natural gas compressor to be isolated for blowdown and maintenance, said selector valve additionally operably coupled to receive said captured fugitive emissions gas, said selector valve also operably coupled to discharge said captured fugitive emissions gas to said captured fugitive emissions gas inlet, said selector valve also operably coupled to discharge said captured fugitive emissions gas to a speed control assembly;
said speed control assembly fluidly connected to the selector valve and the pump, said speed control assembly containing a plunger, a plunger housing and a spring, said plunger housing containing a finite volume of incompressible fluid, said plunger being hollow at a first end to provide a cavity for said spring, said plunger containing a flow passage that can fluidly communicate with multiple cross-drilled bleed holes, movement of said plunger being halted within said plunger housing when said bleed holes are covered to prevent the escape of said finite volume of incompressible fluid;
said speed control assembly also containing a moveable sleeve, said moveable sleeve allowing a variable distance between said bleed holes and said plunger housing as said moveable sleeve is moved;
said speed control assembly also containing a bell crank and bell crank housing, said bell crank controlling an axial position of said moveable sleeve along said plunger, the axial position of said bell crank determined by pressure acting upon one of a diaphragm, a piston-type actuator, an electronic solenoid, or a servo driven actuator; and
a priority valve fluidly connected to the pump, containing a spring on a first side of the priority valve which biases the priority valve to move to a first position which allows two-stage, series-flow operation of the pump;
said priority valve also containing a second gas inlet on a second side of the priority valve fluidly connected to the selector valve which biases the priority valve at a predetermined pressure to overcome the bias of the spring and move to said priority valve to a second position which allows single-stage, parallel-flow operation of the pump;
said priority valve also containing a first gas inlet on the first side of the priority valve which works in conjunction with the spring to urge the priority valve to the first position at the moment the spring bias overtakes a pressure on the second side;
said priority valve also containing a fluid connection during the two-stage operation between the priority valve and the two or more minor diameters of the piston on a first side of the pump which brings a volume of the one or more cylinders containing the two or more minor diameters of the piston on the first side of the pump to substantially atmospheric pressure, removing a load acting on said two or more minor diameters of the one or more pistons.
|