| CPC B60W 30/06 (2013.01) [B60W 60/0011 (2020.02); B60W 60/0015 (2020.02); G06V 20/58 (2022.01); G06V 20/586 (2022.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A cognitive sensor-based autonomous parking route search system, the system comprising:
a cognitive sensor configured to obtain cognitive information for determining an existence and a location of an obstacle by sensing a space around a vehicle being driven in an inside of a parking lot;
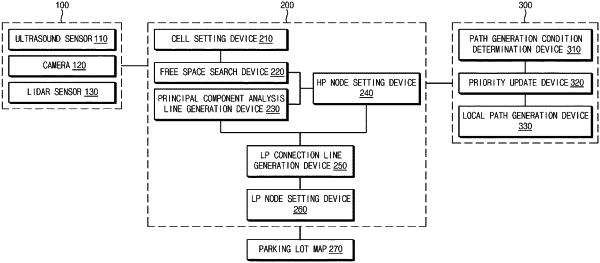
a global path search module configured to generate a global path for the inside of the parking lot as a node map by searching for a free space, in which the vehicle is capable of being driven, based on the cognitive information and by setting a node in the free space; and
an optimal local path generation module configured to generate an optimal local path from a current location of the vehicle to a destination by connecting the node set in the free space while the vehicle moves inside the parking lot;
wherein the global path search module comprises:
a cell setting device configured to determine whether the obstacle is recognized for each cell by dividing the space around the vehicle detected by the cognitive sensor into a plurality of cells;
a free space search device configured to distinguish between a parking space, in which the obstacle is detected, and a free space, in which the obstacle is not detected, based on the cognitive information, to search for a driving free space, which has a width at which the vehicle is capable of being driven, in the free space, and to select the driving free space as a part of the global path; and
a high-priority (HP) node setting device configured to generate a HP node at an end of the driving free space, and to set the HP node for the driving free space on a parking lot map indicating the inside of the parking lot so as to be stored;
wherein the HP node setting device is configured to generate an HP connection line connecting a center of the vehicle to an HP node set in the driving free space so as to be stored; and
wherein the optimal local path generation module comprises:
a priority update device configured to lower a priority of the HP node, through which the vehicle passes while being driven inside the parking lot, in inverse proportion to elapsed time; and
a local path generation device configured to generate a path from the current location of the vehicle to the destination based on a potential field and to generate a path with a high priority of the HP node through which the vehicle passes to reach the destination as a local path.
|