| CPC A61N 1/36135 (2013.01) [A61B 5/0031 (2013.01); A61B 5/0042 (2013.01); A61B 5/14532 (2013.01); A61B 5/14546 (2013.01); A61B 5/318 (2021.01); A61B 5/369 (2021.01); A61B 5/398 (2021.01); A61B 5/4094 (2013.01); A61B 5/686 (2013.01); A61B 5/7225 (2013.01); A61B 5/7275 (2013.01); A61B 5/7282 (2013.01); A61N 1/0456 (2013.01); A61N 1/0476 (2013.01); A61N 1/0529 (2013.01); A61N 1/0551 (2013.01); A61N 1/36 (2013.01); A61N 1/36031 (2017.08); A61N 1/36034 (2017.08); A61N 1/36057 (2013.01); A61N 1/36139 (2013.01); A61N 1/3756 (2013.01); G06N 20/00 (2019.01); A61N 1/37514 (2017.08); A61N 1/3787 (2013.01)] | 13 Claims |
|
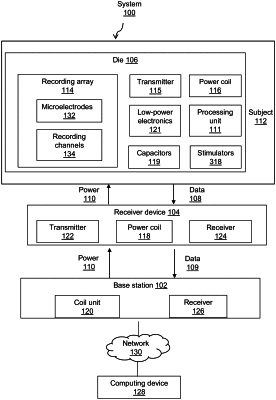
1. A neurostimulator, the neurostimulator implantable or wearable on a subject, the neurostimulator comprising:
a power circuit for providing electrical power to the neurostimulator;
a recording array having a plurality of electrodes for recording a plurality of neurophysiological signals corresponding to a plurality of sites of the subject;
a signal processor configured to:
determine a phase synchrony among the neurophysiological signals; and
associate selected phase synchrony calculations with the prediction or detection of a neurological or neurophysiological condition; and
one or more stimulators for delivering to the subject a stimulation in response to the predicted or detected condition,
wherein the stimulation comprises generating and applying an arbitrary current-mode waveform to a subset of the stimulators and wherein the arbitrary current-mode waveform is generated by a waveform generator that provides the signal and its derivative for use in the calculation of phase synchrony.
|