| CPC A61M 1/3639 (2013.01) [A61M 1/3623 (2022.05); A61M 1/3653 (2013.01); A61M 2205/3331 (2013.01)] | 31 Claims |
|
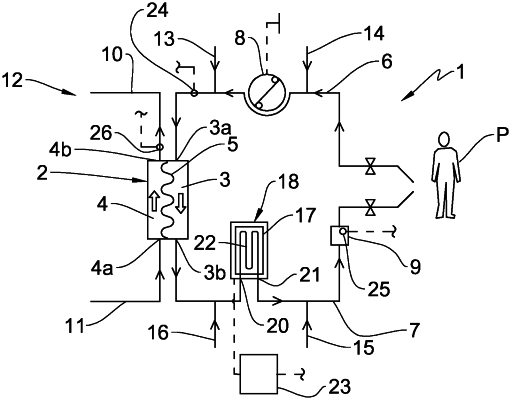
1. Extracorporeal blood treatment apparatus, comprising:
a blood treatment device;
an extracorporeal blood circuit coupled to the blood treatment device and comprising a blood withdrawal line connected to a blood inlet port of the blood treatment device and blood return line connected to a blood outlet port of the blood treatment device;
a blood pump, wherein a pump section of the extracorporeal blood circuit is configured to be coupled to the blood pump;
a first pressure sensor located in a first measurement site on the on the blood withdrawal line upstream of the blood treatment device;
a second pressure sensor located in a second measurement site on the blood return line downstream of the blood treatment device;
an electronic control unit operatively connected to the first pressure sensor and to the second pressure sensor, wherein the electronic control unit is configured to:
receive, from the first pressure sensor, a signal correlated to a measured blood pressure in the first measurement site;
receive, from the second pressure sensor, a signal correlated to a measured blood pressure in the second measurement site; and
correct the measured blood pressure of at least one of:
the first pressure sensor through a mathematical correction model to obtain an actual blood pressure in a first reference site other than the first measurement site, wherein a first circuit section is positioned between the first reference site and the first measurement site, and the mathematical correction model is a model of at least one pressure drop in the first circuit section; and
the second pressure sensor through a mathematical correction model to obtain an actual blood pressure in a second reference site other than the second measurement site, wherein a second circuit section is positioned between the second reference site and the second measurement site, and the mathematical correction model is a model of at least one pressure drop in the second circuit section.
|