| CPC A61B 5/02 (2013.01) [A61B 5/02007 (2013.01); A61B 5/02108 (2013.01); A61B 5/026 (2013.01); A61B 5/027 (2013.01); A61B 5/7278 (2013.01); A61B 6/032 (2013.01); A61B 6/504 (2013.01); A61B 6/507 (2013.01); A61B 6/5217 (2013.01); G16H 50/50 (2018.01); A61B 5/7246 (2013.01); A61B 6/50 (2013.01); Y02A 90/10 (2018.01)] | 30 Claims |
|
11. A method for determining cardiovascular information for a patient using at least one computer system, the method comprising:
retrieving, using at least one processor, data for a plurality of patients of a general population;
dividing, using the at least one processor, the general population into a tuning population and a testing population;
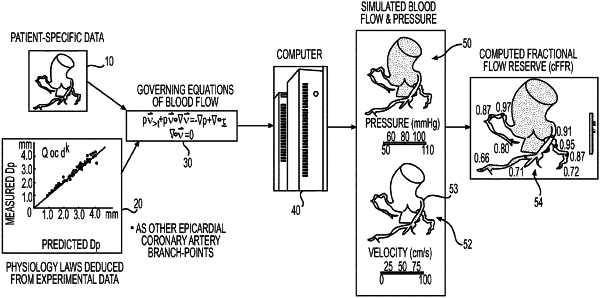
retrieving, using the at least one processor, data for each of a plurality of patients of the tuning population, the data including an invasively obtained measurement of a blood flow characteristic for each of the plurality of patients of the tuning population and a blood flow characteristic computed based at least in part on a respective boundary condition for each of the plurality of patients of the tuning population;
determining, using the at least one processor, boundary conditions tuning characteristics by iteratively comparing the computed blood flow characteristic for each of the plurality of patients of the tuning population to the invasively obtained blood flow characteristic measurement of a respective patient of each of the plurality of patients of the tuning population;
testing the boundary conditions tuning characteristics for each of a plurality of patients of the testing population different form the tuning population based on comparisons between non-invasively computed and invasively obtained blood flow characteristic values for each of the plurality of patients in the testing population;
using the boundary conditions tuning characteristics and a patient-specific anatomical model representing at least a portion of an anatomy of a patient not in the tuning population or the testing population to compute a patient-specific blood flow characteristic value for the patient not in either the tuning population or the testing population; and
outputting the patient-specific anatomical model and the computed patient-specific blood flow characteristic value.
|