| CPC H04W 72/23 (2023.01) [H04L 5/001 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A method for a user equipment (UE) to monitor a physical downlink control channel (PDCCH) for carrier aggregation (CA), the method comprising:
receiving PDCCH candidates in a plurality of configured component carriers (CCs);
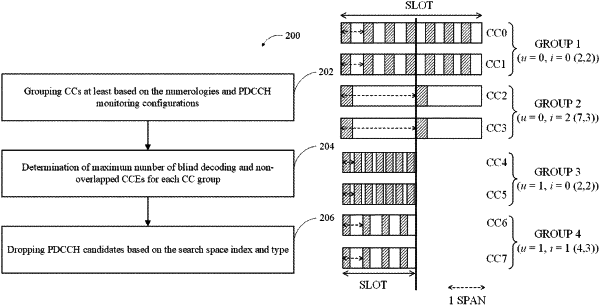
in response to a determination that a maximum number of virtual CCs that the UE is capable of monitoring for PDCCH is smaller than a number of the plurality of configured CCs, grouping the plurality of configured CCs into CC groups based at least in part on subcarrier spacing (SCS) numerologies and PDCCH monitoring configurations corresponding to span patterns within a slot of a downlink (DL) subframe;
determining a maximum number of blind decoding (BD) operations and non-overlapped control channel elements (CCEs) for each of the CC groups; and
monitoring at least a first portion of the PDCCH candidates based on the maximum number of BD operations and non-overlapped CCEs for each of the CC groups.
|