| CPC H04W 56/0005 (2013.01) [H04J 11/00 (2013.01); H04L 5/005 (2013.01); H04L 27/26 (2013.01); H04L 27/2613 (2013.01); H04L 27/2655 (2013.01); H04W 56/00 (2013.01)] | 31 Claims |
|
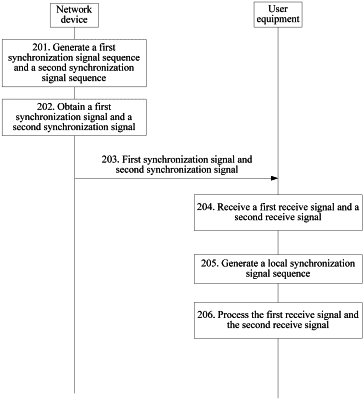
1. An apparatus for wireless communication, comprising:
a communication unit, configured to receive a primary synchronization signal and a secondary synchronization signal,
wherein the primary synchronization signal is based on a primary synchronization signal sequence s(n), and the primary synchronization signal sequence s(n) is based on a sequence c(n), o≤n≤126, a recursion formula of the sequence c(n) satisfies: c(n+7)=(c(n+4)+c(n))mod 2 and the primary synchronization signal sequence s(n) satisfies one of
(n)=1−2·c((n)mod 127);
s(n)=1−2·c((n+43)mod 127); or
s(n)=1−2·c((n+86)mod 127);
wherein the secondary synchronization signal is based on a secondary synchronization signal sequence, and the secondary synchronization signal sequence is based on a sequence f1(n) and a sequence f2 (n), wherein the sequence f1(n) has a same recursion formula as the sequence c(n) and the recursion formula of the sequence f2(n) satisfies: c(n+7)=(c(n+1)+c(n))mod 2, 127 subcarriers in a first orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) symbol are for the primary synchronization signal sequence s(n), and 127 subcarriers in a second OFDM symbol are for the secondary synchronization signal sequence;
a processor, configured to obtain cell identification information based on the primary synchronization signal and the secondary synchronization signal.
|