| CPC H04L 63/20 (2013.01) [H04L 12/4675 (2013.01); H04L 63/0263 (2013.01); H04L 63/0272 (2013.01)] | 16 Claims |
|
1. A computer-implemented method comprising:
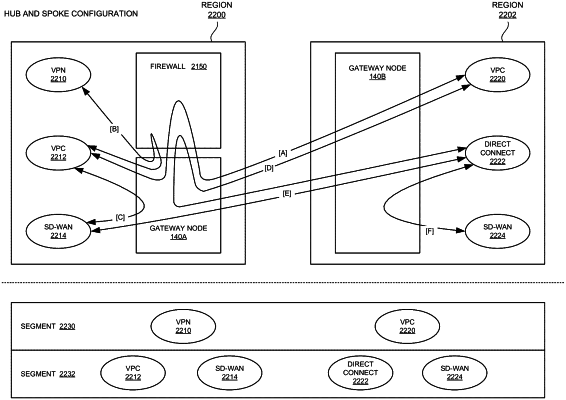
obtaining policy data regarding a private network to be implemented on a cloud provider network, wherein the cloud provider network is organized into a plurality of regions;
determining that the policy data indicates traffic between a first segment of the private network and a second segment of the private requires firewall inspection, wherein each segment of the private network comprises one or more endpoints, wherein a first region of the plurality of regions comprises a first gateway node and a first firewall, and wherein a second region of the plurality of regions comprises a second gateway node; and
deploying, to the first gateway node, first routing criteria specifying that traffic associated with the one or more endpoints in the first segment in the first region and the one or more endpoints in the second segment in the second region is to be routed to the first firewall, wherein second routing criteria deployed to the first gateway node specifies that traffic associated with a first subset of the one or more endpoints in the first segment in the first region and a second subset of the one or more endpoints in the first segment in the second region is permitted without firewall inspection;
wherein the computer-implemented method is executed under control of a computing system comprising memory and one or more computer processors configured to execute specific instructions.
|