| CPC H04L 63/1416 (2013.01) [H04L 63/1425 (2013.01)] | 22 Claims |
|
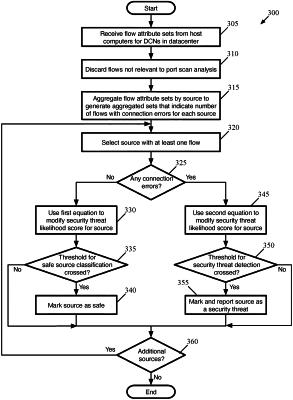
1. A method for identifying malicious actors performing port scans in a datacenter, the method comprising:
from a plurality of host computers in the datacenter, receiving attribute sets for a plurality of flows, each respective attribute set for a respective flow comprising at least (i) a source identifier for the respective flow and (ii) an indicator as to the respective flow is indicative of the source of the respective flow performing a port scan across data compute nodes (DCNs) operating in the datacenter;
for each of a plurality of source identifiers, aggregating the received attribute sets to generate an aggregate attribute set for the source identifier that specifies a number of flows sent by the source during a particular time window that are indicative of the source performing a port scan across DCNs operating in the datacenter; and
for each source identifier of a set of the source identifiers, adjusting an existing security threat likelihood score for the source corresponding to the source identifier by:
in response to detecting no flows indicative of the source performing a port scan are sent by the source during the particular time window, using a first equation that reduces the existing security threat likelihood score for the source; and
in response to detecting at least one flow indicative of the source performing a port scan are sent by the source during the particular time window, using a second, different equation that increases the existing security threat likelihood score for the source: wherein:
each of the first and second equations use (i) a first probability that a flow initiated by a port scanner will not be indicative of its source performing a port scan and (ii) a second probability that a flow initiated by a non-malicious source will not be indicative of its source performing a port scan;
the first equation scales the existing security threat likelihood score for a first source by a ratio of the first probability to the second probability; and
the second equation scales the existing security threat likelihood score for a second source by (i) the number of flows sent by the second source during a particular time window that are indicative of the second source performing a port scan and (ii) a ratio of a probability that a flow initiated by a port scanner will be indicative of its source performing a port scan and to a probability that a flow initiated by a non-malicious source will be indicative of its source performing a port scan.
|