| CPC H04L 43/50 (2013.01) [H04L 43/08 (2013.01); H04W 24/08 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
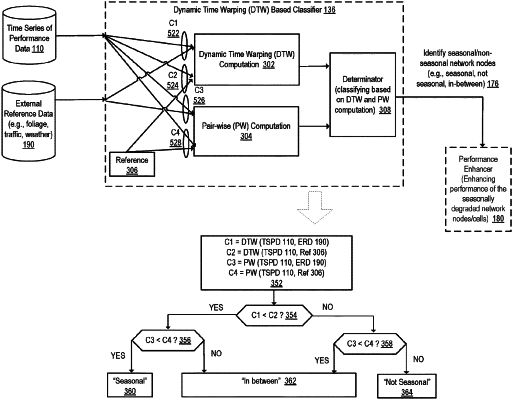
1. A computer implemented method to identify performance seasonality in a network, the method comprising:
obtaining a first plurality of time series of data values, each time series comprising a series of data values corresponding to a performance indicator of one network node within a plurality of network nodes in the network, and the series of data values being ordered in a first periodicity;
obtaining a plurality of series of external reference data values in the first periodicity, each series of external reference data values, ordered in the first periodicity, representing an environmental measure of an area covered by the one network node, wherein each external reference data value within one series of external reference data values maps in time to a data value corresponding to the performance indicator of the one network node at a same time point; and
for a time series of data values, identifying a network node providing the time series of data values as having performance seasonality regarding the performance indicator of the network, when similarity between the time series of data values and a corresponding series of external reference data values meets a criterion based on dynamic time warping distance calculation and pair-wise distance calculation using the time series of data values and the series of external reference data values, wherein the dynamic time warping distance calculates a difference between two sets of data values with an optimal time point alignment, and the pair-wise distance calculates a difference between two sets of data values on the same time points.
|