| CPC H01J 49/164 (2013.01) [H01J 49/0036 (2013.01)] | 9 Claims |
|
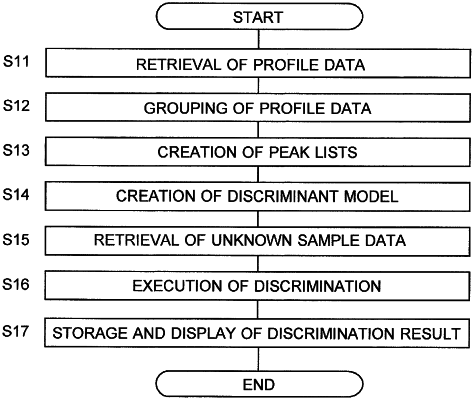
1. A method for processing mass spectrometry data by at least one processor, comprising:
acquiring a plurality of sets of profile data for one known sample by performing laser-light irradiation of the one known sample a plurality of times in a mass spectrometer configured to ionize the one known sample by laser ionization, where each of the plurality of sets of profile data represents a spectrum showing a relationship between m/z values and intensities of ions generated from the one known sample at one of the plurality of times of laser-light irradiation;
sorting the plurality of sets of profile data into a plurality of groups so that each of the plurality of groups includes one or more sets of profile data;
creating, for each of the plurality of groups after sorting the plurality of sets of profile data to form the plurality of groups, a peak list describing an m/z value of each peak originating from the one known sample and an intensity of the same peak based on the one or more sets of profile data included in the group concerned, in which noise removal and peak detection are performed on the one or more sets of profile data when the peak lists are created after the sorting of the plurality of sets of profile data to form the plurality of groups;
creating training data by associating information of the kind of the one known sample with each of a plurality of the peak lists created for the one known sample; and
creating a supervised learning discriminant model for discriminating an unknown sample, using a plurality of the training data obtained by executing the above processes for each of a plurality of known samples.
|