| CPC G16H 50/30 (2018.01) [A61B 5/4842 (2013.01); A61B 5/7275 (2013.01); G01N 24/08 (2013.01); G01R 33/465 (2013.01); A61B 5/055 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
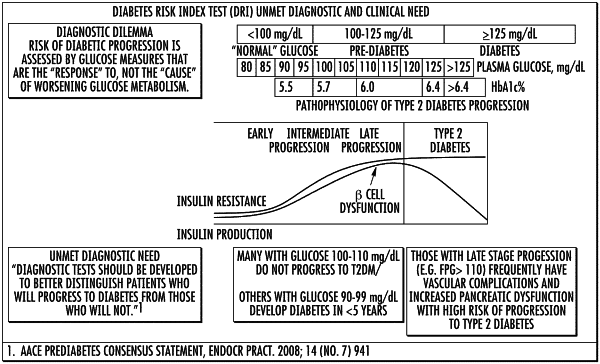
1. A method of evaluating a subject's risk of developing type 2 diabetes and/or having pancreatic beta cell impairment and/or dysfunction, comprising:
providing an in vitro biosample from a subject, wherein the biosample comprises blood, plasma, or serum;
performing Nuclear Magnetic Resonance on the in vitro biosample obtaining an NMR spectrum of the biosample; and
programmatically calculating, using a processor, a short term diabetes risk factor (SDRF) score of a subject using a defined mathematical model of risk of developing type 2 diabetes, wherein the defined mathematical model includes a concentration measurement of a lipoprotein component obtained from the NMR spectrum, a concentration measurement of inflammatory marker GlycA obtained from the NMR spectrum, and an interaction parameter as components of the model which are mathematically combined with respective defined coefficients to generate the calculated SDRF score, wherein the subject is at risk of converting to type 2 diabetes mellitus within 3 years and/or is at risk of beta cell dysfunction when the SDRF score is at a third tertile value or greater value of a study population, wherein GlycA is a composite Nuclear Magnetic Resonance signal from carbohydrate portions of acute phase reactant glycoproteins containing N-acetylglucosamine and/or N-acetylgalactosamine moieties.
|