| CPC G16B 20/00 (2019.02) [A01H 1/04 (2013.01); C12N 15/8261 (2013.01); C12Q 1/6895 (2013.01); G16B 20/50 (2019.02); G16B 40/00 (2019.02); C12N 15/8243 (2013.01); Y02A 40/146 (2018.01)] | 10 Claims |
|
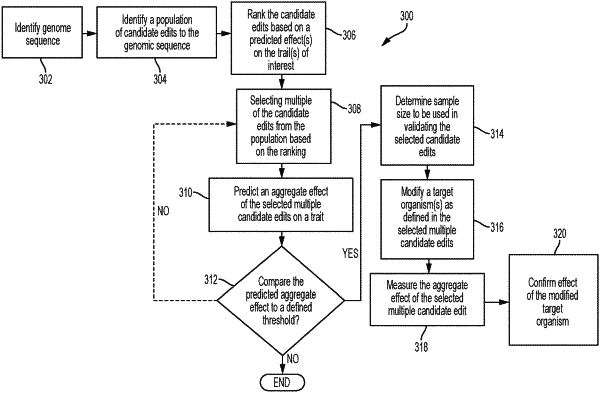
1. A method for predicting a phenotypic impact of multiple genome edits in an organism, the method comprising:
identifying a population of candidate edits to a genomic sequence of said organism based on at least one of genome annotation, genome-wide association study (GWAS) analysis, gene expression data, and a biochemical pathway model;
ranking, by a computing device, each of the candidate edits based on a predicted ability of each candidate edit to affect one or more traits of interest in said organism, the predicted ability based on at least one of a probability of causing an effect, a magnitude of the effect, and a non-parametric classification parameter;
selecting, by the computing device, at least four of the candidate edits based on the ranking;
based on an additive model of predicted effects of the selected at least four of the candidate edits, per type, predicting, by the computing device, an aggregate effect of the selected at least four of the candidate edits for the one or more traits of interest expressed by a specimen of the organism having a genomic sequence and edited according to the selected at least four of the candidate edits, as compared to an unedited specimen of the organism;
determining, by the computing device, a sample size of replicates of the organism to be modified consistent with the selected at least four of the candidate edits for the one or more traits, based on the predicted aggregate effect and a defined probability threshold; and
modifying a number of the replicates of the organism, consistent with the sample size, according to the selected at least four of the candidate edits.
|