| CPC G11C 13/02 (2013.01) [C12P 19/34 (2013.01)] | 8 Claims |
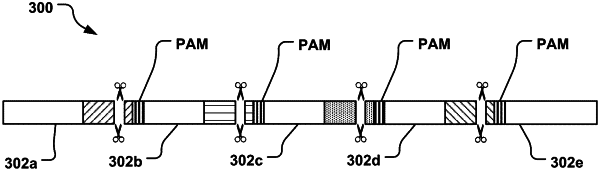
|
1. A method of synthesizing a DNA strand encoding data, the method comprising:
cleaving a DNA backbone having multiple PAM sequences into multiple segments, by moving, via voltage, at least one of the DNA backbone and a set of Cas9 proteins combined with a set of gRNAs across a hydrophobic fluidic platform comprising multiple cells each configured to independently receive a voltage, and combining on the platform the DNA backbone and the set of Cas9 proteins combined with the set of gRNAs at a first location on the platform, resulting in the multiple segments each having terminal ends;
moving across the platform to a second location on the platform, via voltage applied to individual cells, a plurality of data-encoding symbols having terminal ends on the platform;
inserting the symbols between the multiple segments using a homology-directed repair (HDR) process, and
joining the terminal ends of the segments to homologous terminal ends of the symbols in the presence of a ligase or a ligase with a polymerase using another homology-directed repair (HDR) process and forming the DNA strand encoding data comprising alternating segments and symbols.
|