| CPC G06T 11/006 (2013.01) [A61B 5/0073 (2013.01); A61B 5/704 (2013.01); G06T 11/005 (2013.01); A61B 2503/40 (2013.01)] | 19 Claims |
|
1. A system for creating an optical tomographic image of a region of interest of a subject, the system comprising:
(a) a sample stage configured for mounting the subject, the sample stage configured to be in a fixed position in a first condition and to rotate about an axis passing through a center of the sample stage in a second condition;
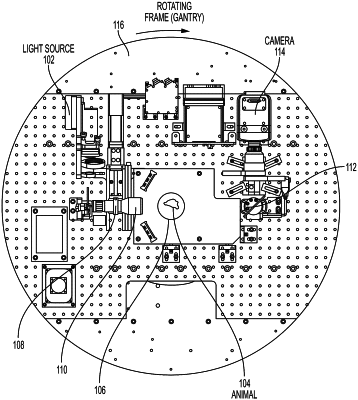
(b) a first source configured to output illumination radiation configured to be directed through a collimator and a beam expander into the region of interest of the subject, wherein the radiation is short-wave infrared radiation (SWIR) having a wavelength from 1000 nm to 1500 nm, the first source is configured to be mounted on a gantry that rotates about the subject in the first condition about an axis that is parallel to the axis passing through a center of the sample stage, and the gantry is fixed in the second condition in which the stage rotates;
(c) a first detector configured to detect radiation from the first source, wherein the detected radiation is radiation transmitted through the region of interest of the subject, the first detector is configured to be mounted on the gantry that rotates about the subject in the first condition, and the gantry is fixed in the second condition in which the stage rotates;
(d) a memory, configured to store a set of instructions; and
(e) a processor configured to execute the set of instructions, wherein the set of instructions when executed by the processor in either the first condition or the second condition:
position the sample stage, the first source, and the first detector with respect to one another so that the first source is positioned to illuminate the region of interest at a plurality of illumination angles and so that the first detector is positioned to detect radiation transmitted through the region of interest at a plurality of detection angles, wherein each of the plurality of detection angles correspond to each of the plurality of illumination angles, and
determine a value of a power of the illumination radiation at each of the plurality of illumination angles, determine a value of a power of the detected radiation at each of the plurality of detecting angles, obtain a plurality of angular projection measurements, wherein each of the plurality of angular projection measurements comprises determining a ratio of the value of a power of the illumination radiation determined at each of the plurality of illumination angles to the power of the illumination radiation determined at each of the plurality of illumination angles, and determine an optical absorption map of the region of interest using data corresponding to the plurality of angular projection measurements, and the processor is further configured to execute the set of instructions, the set of instructions cause the processor to determine a tomographic reconstruction of the optical absorption map of the region of interest.
|