| CPC G06N 20/00 (2019.01) [G01N 27/49 (2013.01); G01N 33/497 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
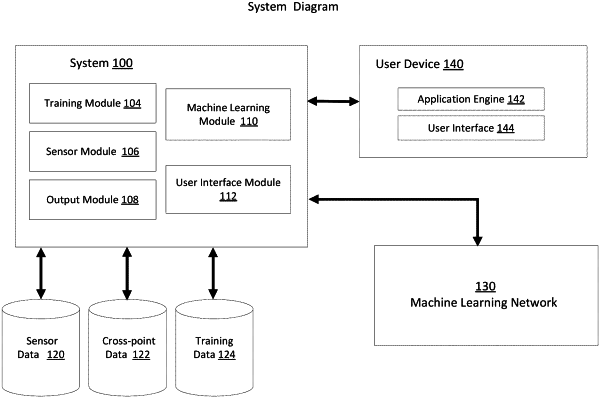
|
1. A computer-implemented method, comprising:
receiving sensor data associated with at least one sensor;
utilizing at least a portion of the sensor data of a respective sensor as input to a machine learning network trained at least on a cross-point observation indicating a response curve location at which response curves at the respective sensor intersect, the response curves corresponding to exposure of the respective sensor to multiple training samples of a same amount of an analyte concentration at a same particular temperature, wherein a variable amount of carbon dioxide concentrations are present across the multiple training samples; and
receiving output from the machine learning network based in part on exposure of the at least one sensor to a present sample having a given concentration of the analyte and a given concentration carbon dioxide.
|