| CPC G06F 21/32 (2013.01) [G06F 2221/2117 (2013.01); H04L 63/0861 (2013.01); H04W 12/06 (2013.01)] | 13 Claims |
|
1. An authentication system, comprising at least one processor; and
at least one memory device that stores a plurality of instructions which, when executed by the at least one processor, causes the at least one processor to:
execute authentication based on pieces of first information registered in advance and pieces of second information associated with the pieces of first information;
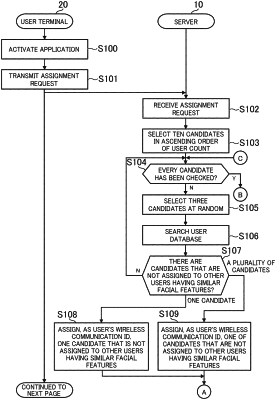
select, when a piece of the second information is to be assigned to a user, a plurality of candidates that are some of a plurality of registered pieces of the second information;
assign, as the user's piece of the second information, one of the plurality of candidates that is unassociated with pieces of the first information that are the same as or similar to a user's piece of the first information;
acquire, for each of the plurality of registered pieces of the second information, a count indicating how many pieces of the first information are associated with the registered piece of the second information, and
select the plurality of candidates by selecting a plurality of pieces of the second information out of the plurality of registered pieces of the second information, in ascending order of the acquired count;
select, when the plurality of candidates selected in ascending order of the acquired count include no candidate that is unassociated with a piece of the first information that is the same as or similar to the user's piece of the first information, at least one next candidate by selecting at least one next piece of the second information in ascending order of the acquired count;
select the candidates at random until a total count indicating a sum of the acquired count acquired for every one of the plurality of registered pieces of the second information reaches a predetermined count.
|