| CPC G06F 16/278 (2019.01) [G06F 16/182 (2019.01); G06F 16/27 (2019.01); G06Q 20/065 (2013.01); G06Q 20/401 (2013.01); H04L 9/0643 (2013.01); H04L 9/50 (2022.05); H04L 2209/56 (2013.01)] | 12 Claims |
|
1. A non-transitory memory device storing instructions that, when executed by a hardware processor of a sharding server in a sharded blockchain, perform operations, the operations comprising:
receiving, by the sharding server, a blockchain-based cryptographic coinage transaction conducted via an internet between a set of computers, wherein the sharded blockchain includes a plurality of blockchain shards, and wherein each blockchain shard of the plurality of blockchain shards is configured to process a different set of simple cryptographic coinage transactions;
determining, by the sharding server, that the received blockchain-based cryptographic coinage transaction is a complex transaction;
in response to determining that the received blockchain-based cryptographic coinage transaction is a complex transaction,
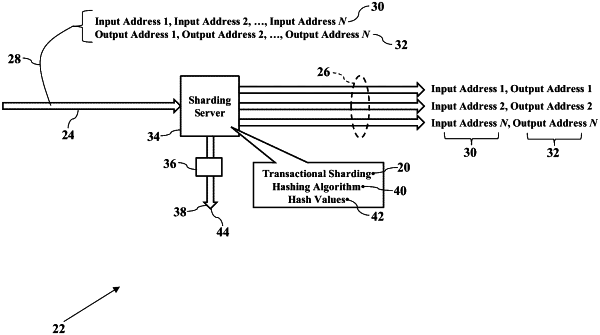
transactionally sharding, by the sharding server, the complex transaction into multiple blockchain-based simple cryptographic coinage transactions, each simple cryptographic coinage transaction being one of
(i) a debit transaction specifying two account addresses on the sharded blockchain, one address of the two account addresses being a temporary account address and a second address of the two account addresses being an input account address, and
(ii) a deposit transaction specifying two account addresses on the sharded blockchain, one address of the two account addresses being the temporary account address, and a second address of the two account addresses being an output account address;
assigning, by the sharding server, each blockchain-based simple cryptographic coinage transaction of the multiple blockchain-based simple cryptographic coinage transactions to a corresponding blockchain shard of the plurality of blockchain shards for processing;
transmitting, by the sharding server, for debit processing, each debit transaction of the multiple blockchain-based simple cryptographic coinage transactions to the debit transaction's corresponding blockchain shard;
determining that all debit transactions of the multiple blockchain-based simple cryptographic coinage transactions debit-processed successfully; and
in response to determining that all the debit transactions of the multiple blockchain-based single cryptographic coinage transactions debit-processed successfully, transmitting each deposit transaction of the multiple blockchain-based simple cryptographic coinage transactions, to the deposit transaction's corresponding blockchain shard for credit processing.
|