| CPC G06F 11/362 (2013.01) [G06F 11/3664 (2013.01); G06F 11/3684 (2013.01); G06F 11/3688 (2013.01); G06F 11/3692 (2013.01); H04L 9/008 (2013.01)] | 16 Claims |
|
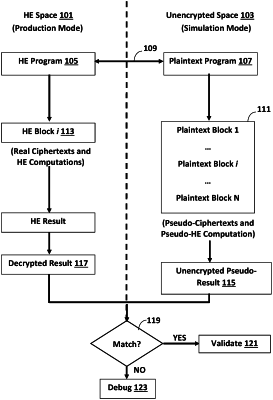
1. A method for debugging a homomorphically encrypted program, the method comprising:
mapping between the homomorphically encrypted program comprising real ciphertext data and encrypted operations in the homomorphically encrypted space and an equivalent plaintext program comprising plaintext pseudo-ciphertext data and pseudo-encrypted operations in plaintext space that simulate at least some of the real homomorphically encrypted ciphertext data and operations;
in a first full pass, executing the plaintext program comprising the plaintext pseudo-ciphertext data and pseudo-encrypted operations in plaintext space;
in a second partial pass, executing a sampling of the homomorphically encrypted program comprising a subset of the real ciphertext data and operations in homomorphically encrypted space that are equivalent to the plaintext pseudo-ciphertext data and pseudo-encrypted operations;
comparing the results of the subset of the real ciphertext data and operations in the first pass of the HE program and the equivalent plaintext pseudo-ciphertext data and pseudo-encrypted operations in the second pass of the plaintext program;
if the compared results match, validating the homomorphically encrypted program and if the compared results do not match debugging the mapping between the homomorphically encrypted program and the plaintext program; and
repeating each pass for a plurality of iterations of increased fidelity by encoding each value with a relatively increased number of floating points corresponding to a relatively increased fixed precision or reduced allowable error, wherein in each sequential iteration accuracy requirement for the results to match increases.
|