| CPC G01V 20/00 (2024.01) [E21B 43/08 (2013.01); E21B 47/0025 (2020.05); E21B 47/113 (2020.05); G01V 3/26 (2013.01); G01V 3/38 (2013.01); G06F 30/20 (2020.01); E21B 2200/20 (2020.05); G06F 2111/10 (2020.01); G06F 2113/08 (2020.01)] | 15 Claims |
|
1. A method for monitoring waterfront movement in a subsurface formation, the method comprising:
using a computer processor:
performing forward modeling of at least one deep low-frequency electromagnetic survey of the waterfront movement,
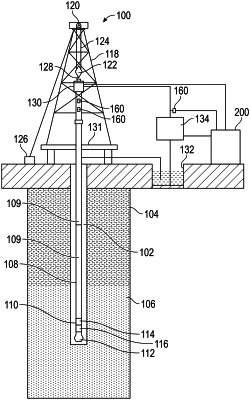
determining, based on the forward modeling, locations for installing at least one electrically insulating spacer between a plurality of well liners to form at least one on-demand electromagnetic source electrode,
determining, based on the forward modeling, locations for installing at least one electrically insulating spacer between a plurality of well liners to form at least one on-demand electromagnetic receiver electrode, and
predicting, based on the forward modeling, a repeat survey time interval;
during well completion:
installing the at least one electrically insulating spacer between the plurality of well liners in a reservoir to form at least one on-demand electromagnetic source electrode, and
installing the at least one electrically insulating spacer between the plurality of well liners in a reservoir to form at least one on-demand electromagnetic receiver electrode;
electromagnetically performing waterfront surveys separated by the repeat time interval, wherein performing comprises: conveying into a well at least one production logging tool that temporarily converts the plurality of well liners into at least one on-demand electromagnetic source electrode and at least one on-demand receiver electrode, wherein temporarily converting the plurality of well liners into at least one on-demand electromagnetic source electrode comprises applying a low-frequency electrical signal,
determining spatial distribution of resistivity and spatial distribution of permittivity based on inverse modeling of the waterfront survey; and
producing, based the inverse modeling, a water saturation image.
|