| CPC G01S 7/497 (2013.01) [G01S 17/894 (2020.01); G01S 17/931 (2020.01)] | 8 Claims |
|
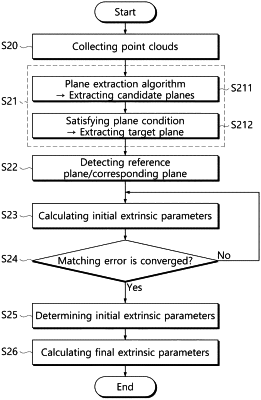
1. An extrinsic calibration method of multiple 3D LiDAR sensors for an autonomous navigation system having a processor, the method comprising:
collecting, by the processor, point clouds by each of the multiple 3D LiDAR sensors;
extracting, by the processor, a plurality of target planes corresponding to a plane from the point clouds of each of the 3D LiDAR sensors;
by using the target plane of any one of the multiple 3D LiDAR sensors as a reference plane, detecting, by the processor, a corresponding plane from the target planes of each of the remaining of the 3D LiDAR sensors on the basis of a similarity with the reference plane;
calculating, by the processor, initial extrinsic parameters for matching between the reference plane and the corresponding plane on the basis of plane parameters of the reference plane and the corresponding plane corresponding to each other;
calculating, by the processor, final extrinsic parameters that minimize variance of measurement points for the reference plane and the corresponding plane corresponding to each other, on the basis of the initial extrinsic parameters; and
correcting the point clouds of the multiple 3D LiDAR sensors based on the final extrinsic parameters,
wherein the extracting of the plurality of target planes comprises:
extracting candidate planes corresponding to a plane from the point clouds for each of the 3D LiDAR sensors through a plane extraction algorithm previously registered; and
extracting, as the target plane, a candidate plane that satisfies a predetermined plane condition from among the candidate planes, and,
wherein the plane condition is expressed as a following equation:
Pλ=(λ2−λ3)/λ1≥Pλ,thr
λ3≤λthr
n≥nthr
(where, Pλ is a planarity of the candidate plane, Pλ, thr is a predetermined reference planarity, λ3is variance in a normal direction of the candidate plane, λthr is a predetermined reference variance, n is a number of point clouds constituting the candidate plane, and nthr is a predetermined reference number and λ1 and λ2 are variance in two axes which are vertical relative to the normal direction of the candidate plane, respectively).
|