| CPC G01R 33/56308 (2013.01) [G01R 33/5601 (2013.01)] | 12 Claims |
|
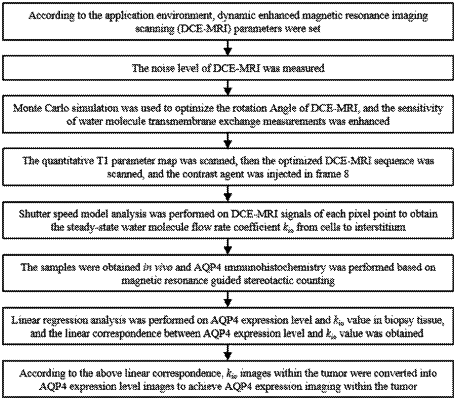
1. A measurement method of intracellular water transmembrane efflux rate (kio), which is not for disease diagnosis, is used as a magnetic resonance imaging biomarker to evaluate the AQP4 expression level of glioma, where in, the measurement method is:
(1) quantitatively measuring the intracellular water transmembrane efflux rate (kio), by using dynamic-contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (DCE-MRI);
(2) using a framed stereotactic biopsy technology to get biopsy tissue and quantitatively measuring its AQP4 expression level;
(3) according to kio and AQP4 expression level, establishing a linear relationship between kio and AQP4; and
(4) quantitatively re-measuring the intracellular water transmembrane efflux rate (kio) of the tissue by using dynamic-contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (DCE-MRI), and the AQP4 expression level of the tissue is obtained according to the linear relationship in step (3).
|