| CPC G01N 33/92 (2013.01) [A61B 5/7275 (2013.01); G01R 33/465 (2013.01); G01N 2570/00 (2013.01); G01N 2800/32 (2013.01); G16H 50/30 (2018.01)] | 30 Claims |
|
1. A method of determining a risk parameter for cardiovascular disease (CVD) or events, comprising:
providing a Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectrum of an in vitro biosample comprising blood, plasma, or serum from a subject;
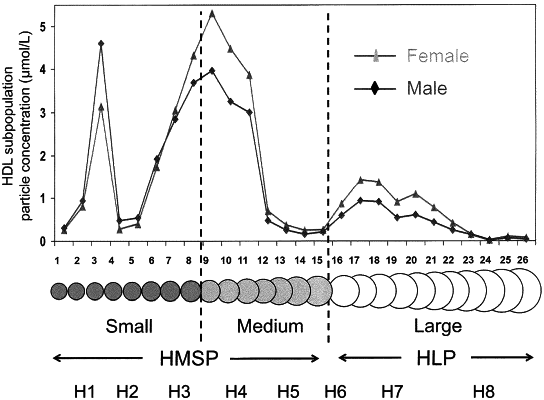
obtaining measurements of HDL particles and inflammatory biomarker GlycA in the biosample;
determining NMR-derived concentrations for an HDL particle size subclass and GlycA, based on the measurements;
programmatically calculating a risk parameter value ((HxI)CVD) of the subject using the NMR-derived concentrations for the HDL particle size subclass and GlycA; and
determining the subject's risk of having and/or developing CVD based, at least in part, on the (HxI)CVD risk parameter value.
|