| CPC G01N 3/068 (2013.01) [G01N 3/42 (2013.01); G06T 7/60 (2013.01); G06T 7/74 (2017.01); G06T 2200/04 (2013.01); G06T 2207/20072 (2013.01)] | 16 Claims |
|
1. A method for determining hardness of a material with implementation of three-dimensional imaging, the method comprising the steps of:
a) providing a sample to be tested having an intact surface;
b) making an imprint in the intact surface of the sample by an indentation process comprising a step of pressing an indenter into the intact surface of the sample by applying an indentation force to the indenter, the imprint having an imprint image;
c) measuring the indentation force during the indentation process;
d) releasing the indentation force;
e) removing the indenter away from the imprint;
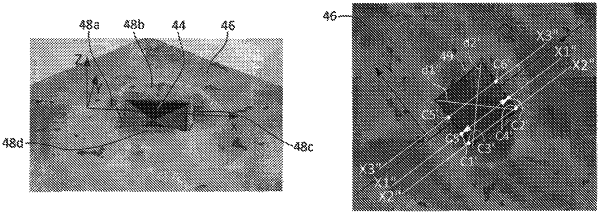
f) obtaining a 3D image of the imprint with the use of an optical system that produces a 3D image of the imprint with an image processor, wherein the image processor presents points on the imprint in the form of a database in a selected orthogonal coordinate system formed by three mutually perpendicular X-axis, Y-axis, and Z-axis;
g) determining a position of the intact surface of the sample beyond the imprint in the aforementioned coordinate system;
h) finding a first pair of points of intersection of an arbitrarily positioned an X1′ axis, the X1′ axis being formed by shifting at least the X-axis in a plane-parallel motion in the direction of the Y-axis across the imprint in a X-Y plane of the intact surface, said first pair of points of intersection coinciding with respective points of the database;
i) repeating the steps h) n times, where n≥2 for finding n pairs of points of intersection;
j) forming, based on the n pairs of points of intersection, a virtual image of the imprint in the X-Y plane of the intact surface;
k) determining from the virtual image of the imprint a reference dimension needed for use in standard formulas for hardness calculation; and
l) calculating the hardness by the standard formulas for hardness calculation by using the reference dimensions.
|