| CPC G01N 27/82 (2013.01) [G01R 33/0047 (2013.01); G01R 33/0094 (2013.01)] | 7 Claims |
|
1. A non-destructive testing device for detecting damage to a steel wire rope, comprising:
a first shell;
a bushing;
an second shell;
an electrical connector;
an air bag;
a PCB; and
a guide wheel
wherein
the bushing limits the first shell and the second shell through a limiting groove, the first shell is connected to the second shell via an opening and closing structure, the air bag is wrapped around the bushing, the PCB is fixed on the second shell or the first shell, and the PCB is connected to the guide wheel through the electrical connector;
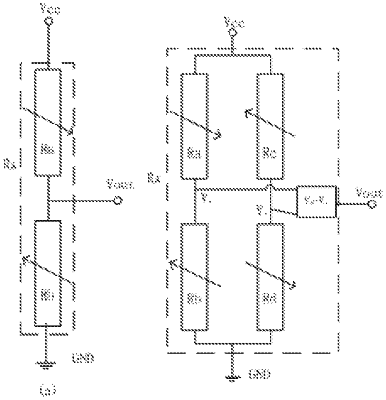
a magnetoresistive sensor array composed of N magnetoresistive sensors is arranged inside the air bag and is uniformly arranged in a circumferential direction of the bushing, a steel wire rope passes through the magnetoresistive sensor array, and when the steel wire rope moves, it drives the guide wheel to rotate and triggers an acquisition of a command;
the guide wheel is set with a position coder which is used to calculate a relative position of movement of the steel wire rope; and
the PCB is connected to a single chip microcomputer via a peripheral interface, and the single chip microcomputer is used to calculate a differential signal of N adjacent magnetoresistive sensors and to determine whether the steel wire rope is damaged.
|