| CPC G01M 5/0041 (2013.01) [G01M 5/0008 (2013.01)] | 13 Claims |
|
1. A derivation method for causing a processor to execute a process, the derivation method comprising executing on the processor the steps of:
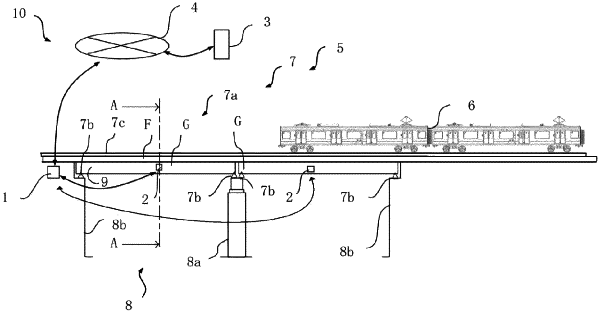
acquiring time-series data including acceleration generated at a predetermined observation point of a superstructure of a bridge as a response caused by a movement of a formation moving vehicle formed with one or more moving vehicles on the superstructure, a value of the acceleration being detected by an acceleration sensor disposed at the predetermined observation point of the superstructure;
acquiring, as environment information, information on a structure length that is a length of the superstructure, a moving vehicle length that is a length of the formation moving vehicle, and an installation position of each of a plurality of wheels of the formation moving vehicle with the superstructure;
deriving an entry time point and an exit time point of the formation moving vehicle with respect to the superstructure, based on the time-series data;
acquiring a number of the one or more moving vehicles formed in the formation moving vehicle;
acquiring an estimated value of a third deflection amount of the superstructure at the predetermined observation point due to a first static response generated as the response, based on the number of the one or more moving vehicles, the entry time point, the exit time point, the environment information, and a deflection model of the superstructure;
deriving a dynamic response at a designated position based on:
a fourth deflection amount normalized by a first vibration component of the dynamic response, the first vibration component corresponding to a difference between the time-series data and the estimated value, the fourth deflection amount being derived based on the deflection model and the first vibration component;
an amplitude ratio of
a first deflection amount that is normalized and indicates a distribution of a vibration amplitude at the predetermined observation point to
a second deflection amount that is the normalized and indicates a distribution of the vibration amplitude at the designated position of the superstructure, the designated position being different from the predetermined observation point;
a second vibration component of the designated position derived based on the first vibration component and the amplitude ratio; and
a second static response of the designated position derived based on the time-series data and the estimated value; and
diagnosing a state of the superstructure of the bridge at the designated position based on the dynamic response.
|