| CPC G01L 1/246 (2013.01) [A41D 1/002 (2013.01); A61B 5/0002 (2013.01); A61B 5/1121 (2013.01); A61B 5/6804 (2013.01); A61B 5/742 (2013.01); A61B 5/746 (2013.01); A41B 11/00 (2013.01); A41B 2400/32 (2013.01); A41D 1/089 (2018.01); A41D 19/0027 (2013.01); A41D 2400/32 (2013.01); A44C 5/0015 (2013.01); A44C 5/0023 (2013.01); A61B 2034/2061 (2016.02)] | 13 Claims |
|
1. A system, comprising:
a centralized unit;
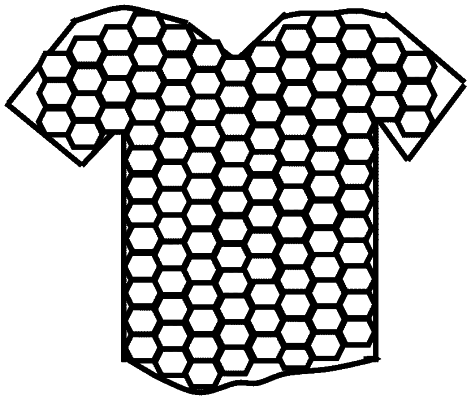
a wearable fabric, comprising:
a plurality of honey-comb structures, wherein each of the honey-comb structure comprising a plurality of adjacently placed hexagon structures,
wherein each hexagon structure comprising a plurality of optical sensor units with each optical sensor unit placed on each side of the hexagon structure, wherein each of the optical sensor unit includes:
a coherent light source,
a Fiber Bragg Grating (FBG),
a photo detector, and
a transmitter;
at least a computation unit configured to:
detect a deformation of a plurality of sides, wherein the plurality of sides corresponds to (i) one hexagon structure or (ii) at least two hexagon structures;
at least a memory to store the detected deformation of the plurality of sides;
wherein the transmitter transmits information related to the detected deformation to the centralized unit,
wherein the centralized unit is configured to:
receive, the transmitted information related to the detected deformation;
generate, signatures of movement patterns of one or more parts of body of a subject in accordance with the detected deformation, wherein the signatures of each of the movement patterns is varied for each of the one or more parts of the body, and wherein the signature for a specific movement pattern is generated based on aggregation of the transmitted information related to the detected deformation;
compare, the generated signatures with stored signatures of movement patterns of the one or more parts of body of the subject, wherein the generated signatures are used to construct an actual trajectory of the one or more parts of body of the subject and the stored signatures includes an expected trajectory of the one or more parts of body of the subject,
wherein the comparison is performed by a trajectory matching algorithm between the actual trajectory and the expected trajectory, and wherein the trajectory matching algorithm uses a multi-layer perceptron (MLP) for linear approximation of the actual trajectory and the expected trajectory;
determine, an error indicative of distortion in the movement patterns of the one or more parts of body of the subject in accordance with a difference between the generated signatures and the stored signatures; and
determine, a range of motion (ROM) of the movement patterns of the one or more parts of the body of the subject, using the error indicative of distortion, wherein the ROM comprises a shoulder ROM, back ROM, thoracic and lumbar ROM, deformity and posture.
|