| CPC G01C 21/3815 (2020.08) [G01C 21/3841 (2020.08); G06V 10/26 (2022.01); G06V 10/82 (2022.01)] | 15 Claims |
|
1. A method for generating map data, the method comprising:
receiving a request to generate an updated map associated with a road network;
generating of a plurality of cells of a real space area, each cell representing a two-dimensional sub-space of the real space area the at least one GPS point received from at least one of a plurality of GPS devices, wherein each of the cells comprise at least one global positioning system (GPS) point, and wherein the real space area comprises the road network;
determining a number of GPS points for each cell of the plurality of cells;
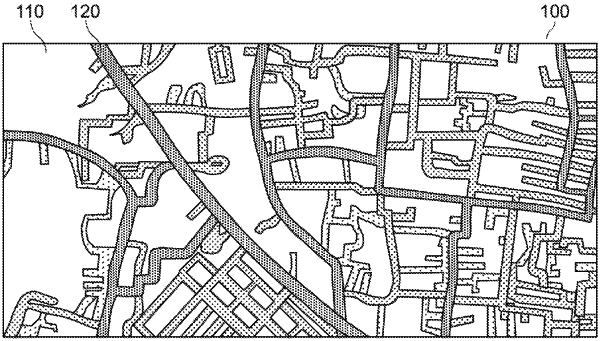
determining a simulated road network based on the numbers of GPS points by analyzing the GPS points using a Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics (SPH) analysis, wherein the cells of the plurality of cells are particles of the SPH analysis and the number of GPS points per cell of the plurality of cells are a scalar of each cell of the plurality of cells in the SPH analysis;
generating at least one visualization image for the distribution of number of GPS points per cell based on the SPH analysis;
updating the simulated road network by classifying each pixel from the generated at least one visualization image to determine whether the pixel is part of a road or not;
providing an input dataset of the road network by labelling all roads where GPS points exist, wherein labels are obtained by querying an open street map (OSM) and retrieving all existing geometries;
generating a binary image in which every pixel has a first label associated to a road or a second label associated to a non-road area by converting the geometries in the image by drawing a plurality of lines on an empty canvas;
comparing the simulated road network determined using the SPH analysis with the road network of the real space area to identify a first set of road segments that exist in the simulated road network that do not exist in the road network of the real space area; and
generating an updated map including the first set of road segments and the road network of the real space area.
|