| CPC F02D 41/0002 (2013.01) [F02D 11/10 (2013.01); F02D 11/106 (2013.01); F02D 41/20 (2013.01); F02D 41/221 (2013.01); F02D 2009/022 (2013.01); F02D 2011/102 (2013.01); F02D 2011/103 (2013.01); F02D 2041/2027 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A system for providing redundant pulse-width modulation (PWM) throttle control, comprising:
a manual throttle controller configured to generate a manual PWM throttle control signal; and
an automated throttle control system, comprising:
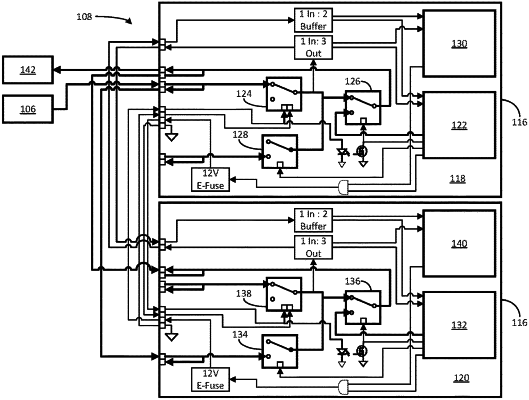
a plurality of automated throttle controllers, each of the plurality of automated throttle controllers being configured to independently control a throttle of a vehicle, and each comprising:
a processor configured to generate and output an automated PWM throttle control signal;
a first double pole double throw (DPDT) relay that, when engaged, is configured to receive and output the manual PWM throttle control signal; and
a second DPDT relay, configured to:
receive and output the automated PWM throttle control signal to an engine, when the second DPDT relay is engaged; and
receive and output the manual PWM throttle control signal to the engine, when the second DPDT relay is disengaged,
wherein:
the plurality of automated throttle controllers includes at least a primary throttle controller and a backup throttle controller, and
at any given time, the automated throttle control system is configured to output, to the engine, one of the following:
the manual PWM throttle control signal;
the automated PWM throttle control signal generated by the primary throttle controller; and
the automated PWM throttle control signal generated by the backup throttle controller.
|