| CPC C03B 23/0252 (2013.01) [B32B 17/10036 (2013.01); B32B 17/10082 (2013.01); B32B 17/101 (2013.01); B32B 17/1011 (2013.01); B32B 17/10119 (2013.01); B32B 17/10137 (2013.01); B32B 17/10761 (2013.01); B32B 17/1077 (2013.01); B32B 17/10788 (2013.01); B32B 17/10889 (2013.01); B60J 1/008 (2013.01); C03B 23/025 (2013.01); C03B 23/03 (2013.01); C03B 23/0357 (2013.01); C03C 3/087 (2013.01); B32B 2250/03 (2013.01); B32B 2250/40 (2013.01); B32B 2605/006 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A laminate comprising:
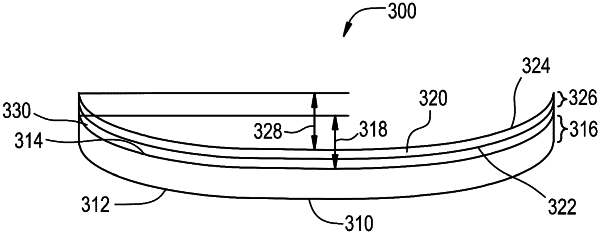
a first curved glass substrate comprising a first major surface, a second major surface opposing the first major surface, a first thickness t1 defined between the first major surface and the second major surface, and the first curved glass substrate comprising a first viscosity;
a second curved glass substrate comprising a third major surface, a fourth major surface opposing the third major surface, a second thickness t2 defined between the third major surface and the fourth major surface, and the second curved glass substrate comprising a second viscosity greater than the first viscosity at a temperature of 630° C., wherein the second thickness is 3.8 mm or greater, wherein the second curved glass substrate is formed by sagging a glass substrate having a length that is greater than or equal to 1.0 m and less than or equal to 3.0 m, wherein the glass substrate comprises a width that is greater than or equal to 0.6 m and less than or equal to 2.0 m, wherein the first curved glass substrate comprises a first sag temperature and the second curved glass substrate comprises a second sag temperature, wherein a difference between the first sag temperature and the second sag temperature is from about 5° C. to about 50° C.;
an interlayer disposed between the first curved glass substrate and the second curved glass substrate and adjacent the second major surface and the third major surface; and
wherein the laminate comprises an effective viscosity between the first viscosity and the second viscosity at a temperature (T) in a range from about 500° C. to about 700° C., the effective viscosity determined by the equation: μeff(T)=((μ1(T)t1)/(t1+t2))+((μ2(T)t2)/(t1+t2)), where μ1(T) is the viscosity of the first curved glass substrate at temperature (T) and μ2 (T) is the viscosity of the second curved glass substrate at temperature (T).
|