| CPC C02F 1/722 (2013.01) [C02F 1/705 (2013.01); C02F 1/76 (2013.01); C02F 2101/106 (2013.01); C02F 2101/18 (2013.01); C02F 2101/20 (2013.01); C02F 2101/36 (2013.01); C02F 2103/06 (2013.01); C02F 2103/10 (2013.01); C02F 2103/18 (2013.01); C02F 2103/365 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
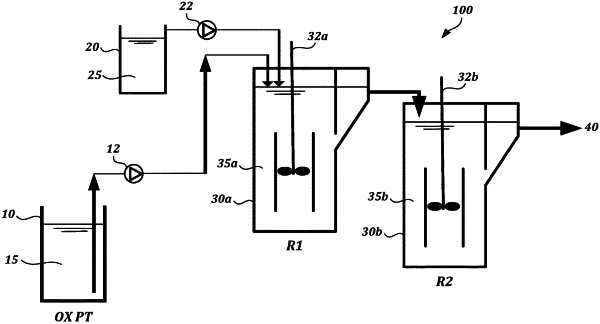
1. A method for reducing the concentration of selenocyanate in water containing selenocyanate, comprising:
in a first step, treating water containing selenocyanate with an oxidant for a time sufficient to oxidize the selenocyanate to provide selenium species treatable by a zero-valent iron system in oxidant-treated water, wherein the oxidant is a hypochlorite; and
in a second step, contacting the oxidant-treated water with a zero-valent iron treatment system that comprises (a) a reactive solid comprising zero-valent iron and one or more iron oxide minerals in contact therewith and (b) ferrous iron, wherein the selenium species in the oxidant-treated water treatable by the zero-valent iron system are reduced.
|