| CPC B64D 45/08 (2013.01) [G01S 13/933 (2020.01); G01S 17/933 (2013.01); G05D 1/101 (2013.01)] | 12 Claims |
|
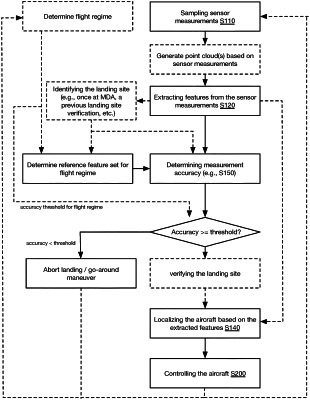
1. A method for controlling an aircraft according to a mission plan which defines a landing site, the method comprising:
automatically controlling the aircraft to execute a go-around maneuver based on a failure to satisfy a confidence threshold;
automatically determining satisfaction of a proximity threshold and, in response:
identifying a set of visual references based on features extracted from measurements collected with a first set of time-of-flight sensors onboard the aircraft, the first set of time-of-flight sensors comprising a LIDAR sensor; and
determining a confidence score value associated with the identification of the set of visual references; and
verifying observability of the landing site with the measurements by a binary determination that the confidence score value satisfies the confidence threshold; and
responsive to the binary determination that the confidence score value satisfies the confidence threshold, automatically controlling the aircraft within an approach corridor of the landing site based on the set of visual references, comprising:
estimating an aircraft state based on a position of at least one of the visual references of the set, wherein the aircraft state is estimated with simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) using the extracted features; and
generating navigational instructions based on the aircraft state, wherein automatically controlling the aircraft to execute the go-around maneuver occurs prior to verifying observability of the landing site.
|