| CPC B60W 30/09 (2013.01) [B60W 30/0956 (2013.01); G06F 18/2193 (2023.01); G06T 7/215 (2017.01); G06T 7/251 (2017.01); G08G 1/166 (2013.01); B60W 2554/40 (2020.02); G06T 2207/20084 (2013.01); G06T 2207/30261 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
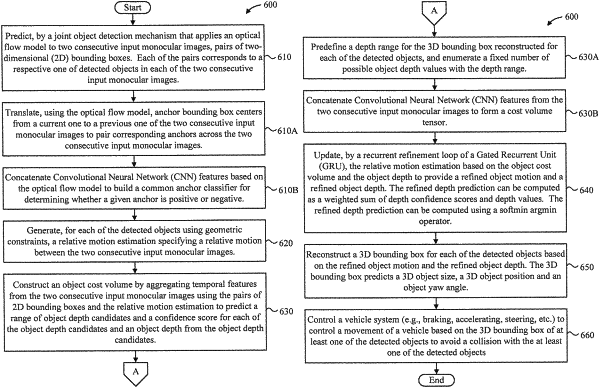
1. A computer-implemented method for three-dimensional (3D) object localization, comprising:
predicting, by a joint object detection mechanism that applies an optical flow model to two consecutive input monocular images, pairs of two-dimensional (2D) bounding boxes, each of the pairs corresponding to a respective one of detected objects in each of the two consecutive input monocular images;
generating, for each of the detected objects using geometric constraints, a relative motion estimation specifying a relative motion between the two consecutive input monocular images;
constructing an object cost volume by aggregating temporal features from the two consecutive input monocular images using the pairs of 2D bounding boxes and the relative motion estimation to predict a range of object depth candidates and a confidence score for each of the object depth candidates and an object depth from the object depth candidates;
updating, by a recurrent refinement loop of a Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU), the relative motion estimation based on the object cost volume and the object depth to provide a refined object motion and a refined object depth; and
reconstructing a 3D bounding box for each of the detected objects based on the refined object motion and the refined object depth, the 3D bounding box predicting a 3D object size, a 3D object position and an object yaw angle.
|